Lingenfelter’s Steamboats on the Colorado River, 1852–1916 provides an implicit social and economic history of every settlement that grew—or faded—along the river’s banks. The book’s narrative threads the growth of these river communities directly to the rise and fall of steamboat commerce.

Yuma and Arizona City
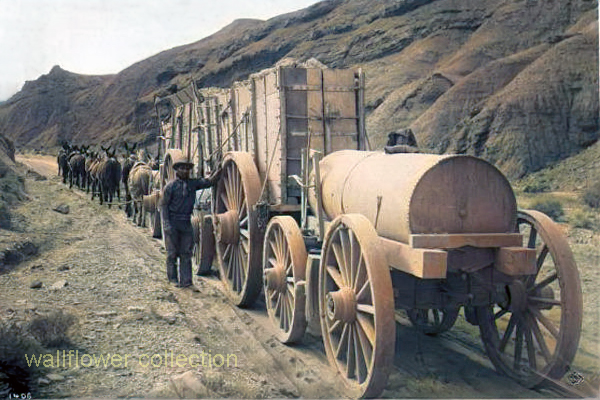
- Origins: Fort Yuma (established 1850) was the main reason steamboats came to the river at all. Its chronic supply shortages prompted the launch of the Uncle Sam in 1852—the first river steamer.
- Growth: Johnson’s General Jesup and later steamers transformed the isolated post into a trade hub. Yuma Indians, Cocopahs, and early merchants (Louis Jaeger, George Hooper, Mrs. Bowman “the Great Western”) were central to its development.
- Outcome: Arizona City (later Yuma) became the permanent entrepot for the Arizona interior, surviving floods that wiped out rival settlements (Jaeger City and Colorado City) in 1862.
- Steamboat impact: Yuma existed because of river transport—its food, freight, mail, and even building materials came upriver. The steamboat wharf and wood yards formed its economic heart until the Southern Pacific Railroad bridge was completed in 1877.
Fort Mohave and the Mojave Valley
- Military anchor: Established in 1859 after Lt. Col. Hoffman’s expedition. Johnson’s General Jesup and Colorado carried the troops and artillery upriver.
- Settlement influence: The fort’s constant freight and troop movements supported a network of wood-cutters, ferrymen, and small traders. Mohave and Chemehuevi Indians interacted with the garrison, at first through hostility, later trade.
- Mining connection: Steamboats supplied nearby mining districts such as Eldorado Canyon, which developed into a key upriver port. Freight was landed directly from San Francisco via Johnson’s line, showing how the steamboat system enabled northern Arizona’s first mineral exploitation.
Ehrenberg (originally Mineral City)
- Origins: Founded in the 1860s as a wood yard and landing above La Paz.
- Growth: When gold was discovered at La Paz (1862), Johnson’s boats (Cocopah, Gila) ran regular trips, and the landing evolved into Mineral City—later renamed Ehrenberg.
- Economic role: It became the principal upriver port for western Arizona mining. Merchants, assay offices, and stage connections tied it to Prescott and Wickenburg.
- Decline: As river levels shifted and the railroad advanced toward Needles, Ehrenberg’s role diminished; by the 1890s, it had reverted to a small ferry and freight stop.
La Paz
- Discovery and boom: Founded after the 1862 placer rush at Laguna de la Paz, fifty miles above Yuma.
- Steamboat role: Johnson’s Cocopah and Colorado II made it a thriving port for a few years; millions in gold dust and supplies moved through its landing.
- Community effects: Temporary but intense—stores, saloons, and a post office sprang up almost overnight. The town declined after the placers gave out, though it remained a shipping point for freighting routes into central Arizona.
Callville and Eldorado Canyon
- Callville: Established in 1864 by Mormons under Anson Call as the uppermost navigable landing on the Colorado. Johnson’s Mojave II and the Gila reached it with supplies for Mormon colonies.
- Eldorado Canyon: The river link to Nevada’s silver mines. Steamers delivered ore machinery and carried bullion out. Lower Camp and Hardyville (later Bullhead City) also grew as logistical points for these mines.
- Outcome: The decline of mining and the development of railroads at Needles ended their importance, but their brief steamboat era left physical and place-name legacies.
Hardyville, Needles, and the Mojave Crossing
- Hardyville: Founded by William Hardy in the 1860s near Fort Mohave as a landing and ferry for freight into northern Arizona and served by Johnson’s and later Polhamus’s boats (Gila, Mohave II).
- Needles: Grew later from the same corridor once the railroad bridged the river. For a time, both rail and steamboat freight were interdependent—boats ferried heavy goods to and from the rail terminus.
- Cultural tie: These settlements owed their early survival to the steamboat’s ability to deliver goods to otherwise inaccessible desert outposts.
Mexican Delta Settlements
- Robinson’s Landing and Port Isabel: Transfer points where sea-going schooners met the river steamers. These landings, although primitive, were the logistical lifeline between San Francisco and Arizona before the rail era.
- Cocopah and Yuma labor: River tribes provided the essential wood-cutting and loading labor at these lower landings. The steamboat economy reshaped indigenous life, drawing them into the wage economy.
- Later decline: When the Imperial Canal and Laguna Dam diverted the river (1905–1909), most of these delta landings were abandoned or submerged.
Imperial Valley and the Lower Colorado (20th century)
- Engineering phase: The Searchlight and St. Vallier were used by the California Development Company and the Reclamation Service to ferry materials during the Imperial Valley flood and Laguna Dam projects (1905–1909).
- New communities: Mexicali, Calexico, and Imperial grew directly from these river engineering efforts—the last chapter of the steamboat’s social influence.
Summary of Broader Community Ties
- Military Supply: Forts Yuma and Mohave created permanent river commerce.
- Mining Support: Steamboats connected isolated camps—La Paz, Eldorado, Callville—to coastal markets.
- Civic Formation: Yuma, Ehrenberg, and Hardyville evolved from wharves and woodyards into lasting towns.
- Cross-Cultural Exchange: Cocopah, Yuma, and Mohave tribes were drawn into trade and labor systems, profoundly altering their economies.
- Transition and Legacy: As railroads and dams replaced steamers, most of these towns either adapted (Yuma, Needles) or faded (La Paz, Callville).
In essence, the steamboats were the architects of civilization along the Colorado River. Every settlement from the Gulf to Callville began as a landing, woodyard, or ferry point tied to the fleets of Johnson, Polhamus, and their successors. When the engines fell silent in 1916, the towns they had spawned remained—the permanent human footprint of the river’s steamboat age.
Timeline of Steamboats and River Communities along the Colorado River, 1539–1916
(based on Richard E. Lingenfelter, Steamboats on the Colorado River, 1852–1916, University of Arizona Press, 1978)
1539 Francisco de Ulloa becomes the first European to sight the mouth of the Colorado River while exploring the Gulf of California for Spain.
1540 Hernando de Alarcón sails into the river delta, establishing it as a navigable waterway in Spanish maps.
1781 Mission San Pedro y San Pablo de Bicuñer is founded near the river and soon destroyed in native uprisings; Spanish efforts to settle the lower Colorado end.
1849 California Gold Rush brings heavy overland migration; Dr. Lincoln establishes a ferry at Yuma Crossing to serve travelers heading to the gold fields.
In 1850, Fort Yuma was founded to protect emigrants; supplies were freighted overland at ruinous cost.
In 1850, Lt. George H. Derby attempted to deliver supplies by sea aboard the schooner Invincible but failed due to Hardy’s erroneous map of the Colorado estuary.
In 1852, Captain James Turnbull launched the Uncle Sam, the first steamboat on the Colorado River, assembled near the mouth. She reaches Fort Yuma in December but later sinks.
In 1853, George A. Johnson, Ben Hartshorne, and Captain Alfred Wilcox established a freight company and began regular steam navigation with the General Jesup in January 1854.
1854 General Jesup proves commercial success; Fort Yuma and nearby settlements (Yuma Crossing, Jaeger’s Ferry) grow rapidly.
1855–1856 Additional woodyards established along the lower river; Johnson expands his business.
In 1857, Lt. Joseph C. Ives is assigned to explore the river’s head of navigation with the steamer Explorer.
In 1858, Ives launches the Explorer and ascends the river to Black Canyon; George Johnson’s General Jesup reaches nearly the same point earlier, demonstrating practical navigation to Pyramid Canyon.
In 1859, Fort Mohave was established at Beale’s Crossing; Johnson’s Colorado and Cocopah transport troops and supplies upriver. The Mohaves subdued after brief hostilities.
1859 Cocopah launched, the largest and most powerful stern-wheeler on the river to date; it began freight runs between the Gulf and upriver forts.
1860 Steamers in regular service to both Fort Yuma and Fort Mohave; landings and wood-yards form the nuclei of new settlements.
1861 Johnny Moss discovers silver in Eldorado Canyon; the first mining boom supported by river transport begins.
1862 Great Colorado River gold rush; La Paz and Mineral City (later Ehrenberg) were established as upriver mining and freight centers. Yuma (Arizona City) grows rapidly.
1863 Arizona Territory created; steamboats supply frontier posts, mines, and settlements along the river corridor.
In 1864, Mormon colonists founded Callville as the uppermost navigable port on the river; Mohave I and Gila reached it with freight and supplies.
1864–1865 Floods destroy Jaeger City and Colorado City; Arizona City (Yuma) survives and becomes the dominant port.
1866 Hardyville (later Bullhead City) founded as river landing and ferry opposite Fort Mohave.
1867–1870 Johnson’s fleet expanded with Cocopah II, Mohave II, Gila, and Colorado II; regular commercial runs between Gulf and Hardyville.
1870s Ehrenberg (formerly Mineral City) and La Paz prosper as supply depots for mining districts. Yuma thrives as regional capital and customs point.
1877 Southern Pacific Railroad reaches Yuma; rail begins to replace river freight to Fort Yuma and interior Arizona.
1880s Decline of Johnson’s monopoly; smaller independent boats like Searchlight and St. Vallier begin service for construction and local trade. Needles develops as rail terminal at Mojave Crossing.
1890s Limited steamboat service continues for miners and settlers between Yuma and Needles; smaller upper-river craft like Undine and Comet work in Green and Glen Canyons.
1905 Catastrophic flooding of the Imperial Valley (Salton Sink) creates major river diversion works. Steamboats carry rock, equipment, and workers to repair the break.
1907–1909 Construction of Laguna Dam; dredges Alpha, Beta, and Delta assist in engineering works. River settlements (Mexicali, Calexico, Imperial) expand.
1910–1916 Final years of commercial operation; the Searchlight and St. Vallier continue limited freight and survey work.
1916 Steamboat era ends; the last operational vessel, Searchlight, retires. The Colorado’s navigation frontier gives way to railroads and irrigation infrastructure.
Summary:
The river towns—Yuma, La Paz, Ehrenberg, Hardyville, Callville, and others—each owe their existence to this 64-year steamboat epoch. The boats linked mining, military, and agricultural settlements from the Gulf of California to southern Nevada, and their decline marked the end of the Colorado River as an open commercial highway.
Connectivity along the Colorado River, 1852–1916
(based on Richard E. Lingenfelter’s Steamboats on the Colorado River, 1852–1916, University of Arizona Press, 1978)
The Colorado River functioned as a living transportation spine for the American Southwest. From the Gulf of California to the mouth of the Virgin River, its steamboat era linked ports, mines, forts, and settlements into a single continuous system of movement and exchange. The following summarizes how this connectivity developed—its physical, economic, and cultural dimensions.
1. The River as Transportation Artery
Before railroads, the Colorado was the only practical route through an otherwise impassable desert frontier. Steamboats transformed it from a natural barrier into a corridor of movement:
- Vertical Integration: Cargoes from San Francisco and Mexican ports entered at the Gulf of California and were transferred at Robinson’s Landing or Port Isabel to shallow-draft river steamers.
- Main Route: Steamers ran 600 miles upriver from the estuary to the head of navigation at Callville, with landings every 25–40 miles at woodyards and supply camps.
- Branch Distribution: From these landings, mule and wagon roads carried freight to mining camps—La Paz, Wickenburg, Prescott, Eldorado Canyon, and beyond.
The river linked Pacific maritime trade directly to Arizona’s interior economy, reducing freight costs from $500 a ton (overland) to $75 or less.
2. Economic Connectivity: The Steamboat Network
Each segment of the river supported distinct but interlocking economies:
- Lower River (Gulf to Yuma):
- Served by General Jesup, Colorado I–II, and Cocopah boats.
- Functioned as the supply chain for Fort Yuma, Arizona City, and Cocopah/Yuma tribal labor networks.
- Exports: military supplies outbound; imports: grain, hides, and ore from upriver.
- Middle River (Yuma to Fort Mohave):
- Connected through Gila, Mohave, Cocopah II.
- Supported ranching, freighting, and mining from La Paz, Ehrenberg, and Mineral City.
- Fort Mohave provided stability and demand; nearby Hardyville became the main transfer point to the northern interior.
- Upper River (Fort Mohave to Callville):
- Connected through seasonal navigation, reaching Eldorado Canyon and Callville, linking Mormon settlements and Nevada mines.
- Steamboats supplied machinery, food, and mail to isolated canyons and hauled bullion downstream.
These tiers formed an interdependent flow of goods and people—San Francisco → Gulf → Yuma → La Paz → Hardyville → Callville—binding together three territories: California, Arizona, and Nevada.
3. Military and Strategic Connectivity
- Fort Yuma (1850) and Fort Mohave (1859): Anchored U.S. authority in the region.
- Steamboats like the Jesup and Colorado carried troops, cannon, and supplies upriver, allowing rapid response to uprisings.
- The river served as a military highway, tying remote garrisons into the national supply chain without the need for overland caravans.
4. Cultural and Indigenous Connectivity
- The steamboat economy drew Cocopah, Yuma, Mohave, and Chemehuevi peoples into wage labor as woodcutters, ferrymen, and pilots.
- Traditional seasonal migration routes became part of the logistical system for fuel supply—woodyards spaced every 30 miles were typically operated by natives.
- Cultural exchange was double-edged: it increased trade and communication, but also displacement and dependency.
5. Intermodal and Regional Connectivity
- Overland Links: Freight from landings connected to desert wagon roads—the Ehrenberg–Prescott route, Hardyville–Cerbat road, and Callville–St. George trail.
- Rail Integration: The arrival of the Southern Pacific Railroad at Yuma (1877) and the Atlantic and Pacific line at Needles (1883) converted the river into a feeder route.
- Steamboats ferried rail cargoes across unfinished bridges.
- Yuma and Needles became multimodal junctions, the first in the desert Southwest.
- Engineering Connectivity: During the early 1900s, steamboats carried dredge parts, rock, and machinery for the Imperial Canal and Laguna Dam, linking the river’s navigation legacy to the birth of modern irrigation infrastructure.
6. Communication and Settlement Network
- Mail and Passenger Routes: Regular boat schedules carried mail and travelers between Yuma, Ehrenberg, and Hardyville—functioning as the desert’s postal road.
- Towns and Ferries: Settlements emerged at every refueling stop: Jaeger’s Ferry, Pedrick’s Landing, Ogden’s, Gridiron, Port Famine, Mineral City, Ehrenberg, Hardyville, Callville.
- Urban Continuity: The steamboat corridor produced a “string of pearls” settlement pattern—each landing spaced by distance of a single day’s travel.
7. Decline and Legacy
- Railroads, motorboats, and dams broke the linear chain of river-based transport.
- After 1905, the river was more a site of engineering than navigation.
- Yet Yuma, Needles, and Mexicali owe their placement and early prosperity to this 19th-century river connectivity.
- Even in decline, the steamboat system laid the geographic framework for later highways, irrigation canals, and border cities.
Summary
From 1852 to 1916, the Colorado River connected the American frontier in a single functional system—military, economic, and human.
- The lower river tied the desert to the Pacific.
- The middle River opened Arizona’s mines and ranches.
- The upper river linked the Mormon, Nevada, and Utah frontiers.
Steamboats were not just transport—they were the connective tissue binding a thousand miles of desert into one coherent region. When they vanished, their routes became the blueprint for roads, railways, and settlements that still follow the river’s course today.