The Mojave Desert, an expansive arid region spanning southeastern California and parts of Nevada, Arizona, and Utah, is more than just a vast, desolate landscape. It is a land imbued with a rich cultural history, much of which is etched into the ancient Indian trails that crisscross its terrain. These trails are a deep connection to the land possessed by the indigenous peoples who once called this desert home.
Historical Significance
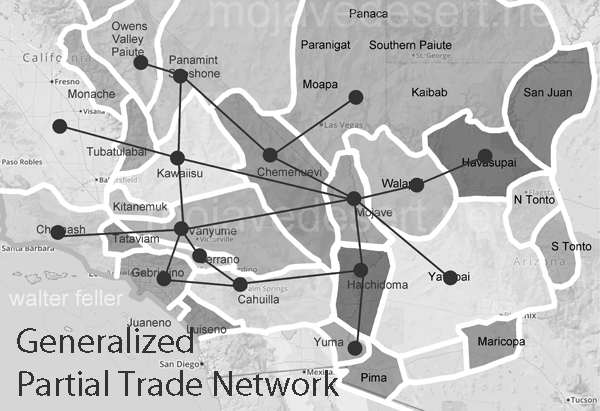
.
The Indian trails of the Mojave Desert were primarily created and used by Native American tribes such as the Mojave, Chemehuevi, and Southern Paiute. These tribes utilized the trails for various purposes, including trade, communication, and seasonal migration. The network of trails facilitated the exchange of goods like pottery, shells, foodstuffs, and obsidian, linking the Mojave Desert with coastal and inland regions. This trade network was integral to the economy and culture of the tribes, allowing for the spread of ideas, technologies, and cultural practices.
The trails were not merely utilitarian. They often held spiritual and cultural significance, following natural landmarks and water sources. Sacred sites, ceremonial grounds, and essential gathering places were often along these trails. This cultural layer adds depth to understanding these pathways, illustrating how they were interwoven with the people’s social and spiritual lives.
The Old Spanish Trail
One of the most notable trails is the Old Spanish Trail, which later became a significant route for Spanish explorers and settlers in the 18th and 19th centuries. Blazed initially by Native Americans, this trail stretched from Santa Fe, New Mexico, to Los Angeles, California. The Spanish utilized these established paths to connect their colonial holdings, facilitating trade and the movement of people and goods. The trail highlights the continuity of use by various cultures over centuries, transforming from an indigenous trade route to a significant conduit of colonial expansion.
The Old Spanish Trail was a challenging route, traversing some of the harshest landscapes in North America. Its use by both Native Americans and later Spanish settlers underscores the adaptability and resourcefulness required to navigate the Mojave Desert.
Adaptation to the Desert Environment

The Indian trails of the Mojave Desert showcase the adaptive strategies of Native Americans to the harsh desert environment. The tribes identified and utilized natural springs and seasonal water sources, ensuring safe passage across the expansive and often unforgiving terrain. These water sources were crucial, as they provided the necessary hydration points along the trails. Knowledge of these water sources was passed down through generations, often guarded closely as essential survival information.
The trails frequently ran along the base of mountain ranges and through passes, providing more accessible routes than the open desert. These paths took advantage of the natural topography to offer shade, easier walking conditions, and strategic viewpoints. The trails also connected various ecological zones, allowing the tribes to exploit various resources, from desert plants to mountain game.
Cultural Legacy
Today, the Indian trails of the Mojave Desert are an integral part of the region’s cultural heritage. Many of these trails are preserved and studied by archaeologists and historians, offering insights into the historical movements and lifestyles of the indigenous populations. Modern-day hikers, historians, and cultural enthusiasts retrace these paths, gaining a deeper understanding of the rich history and enduring legacy of the Native American tribes who first navigated the vast Mojave Desert.
Preservation efforts are crucial in maintaining these historic routes. Many trails are threatened by modern development, off-road vehicle use, and natural erosion. Organizations dedicated to preserving Native American heritage work tirelessly to document and protect these trails, ensuring they remain a living testament to the ingenuity and resilience of the desert’s original inhabitants.
Contemporary Relevance
In recent years, interest has been resurgent in these ancient trails. Educational programs, guided tours, and cultural heritage projects aim to bring the stories of these paths to a broader audience. Indigenous groups also play a vital role in these efforts, sharing their knowledge and perspectives to preserve and respect the trails as sacred cultural sites.
The trails also offer lessons in sustainable living and environmental stewardship. The indigenous peoples of the Mojave Desert thrived in a harsh environment through a deep understanding of the land and its resources. Their trails remind us of the importance of living in harmony with nature, an increasingly relevant lesson today.
Conclusion
The Indian trails of the Mojave Desert are more than just paths across the sand; they are the veins of a rich cultural heritage, connecting the past with the present. They tell stories of trade, migration, survival, and spiritual journeying etched into the desert’s landscape. As we explore and preserve these trails, we honor the legacy of the Native American tribes that first navigated the Mojave Desert, ensuring that their stories and knowledge continue to inspire and educate future generations.
