(1873)
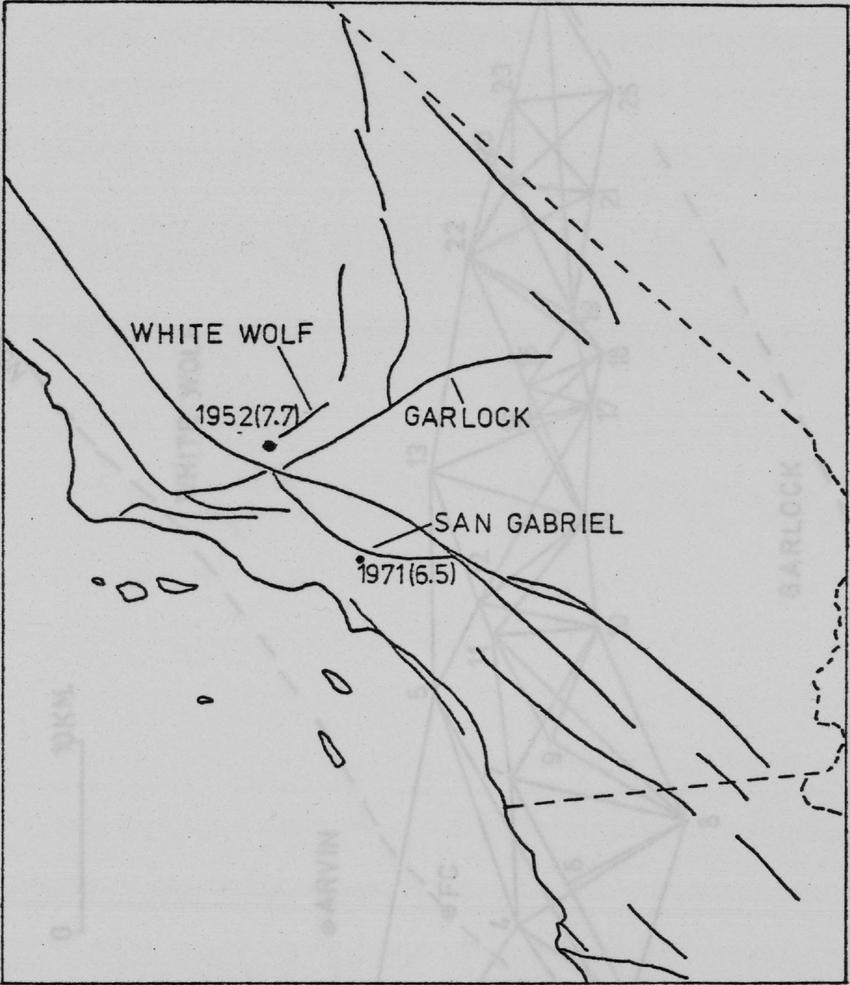
The Von Schmidt boundary, or the Schmidt Line, refers to a historical boundary line in California. It was surveyed and established by Alexey von Schmidt, a Russian engineer, in the 1860s. The purpose of the Von Schmidt boundary was to delineate the border between California and Nevada during a time when there was confusion and disputes over the exact location of the state boundary.
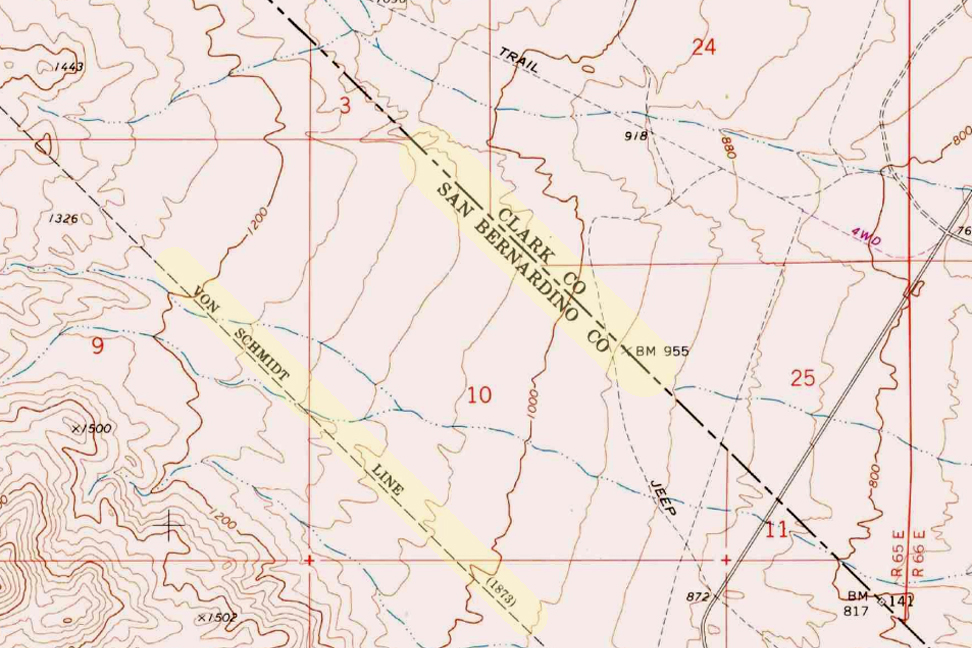
Von Schmidt’s survey helped clarify the boundary and resolve conflicts between California and Nevada. His efforts included placing markers and monuments along the boundary line to make it clear and permanent. The boundary he established still exists today and is the official border between the two states.

The Von Schmidt boundary is of historical significance and has been preserved as a reminder of the surveying and boundary disputes of the past. It is located in the eastern part of California near the Nevada border.
Why was the initial boundary incorrect?
The initial boundary between California and Nevada was incorrect and subject to disputes for several reasons:
- Lack of Accurate Surveys: In the early years of California’s statehood and during the Gold Rush era in the mid-19th century, limited resources and technology were available for accurate land surveys. As a result, the initial surveys and boundary markers were not precise.
- Rush for Mineral Resources: The discovery of gold and other valuable minerals in the region led to a rapid influx of settlers and miners. This rush created a need for clear land boundaries and property rights. However, the focus was often on extracting resources rather than conducting precise surveys.
- Overlapping Claims: Different parties, including miners, settlers, and land speculators, had conflicting claims to land in the region. These overlapping claims added to the confusion regarding the exact location of the state boundary.
- Political Disputes: California became a state in 1850, and shortly thereafter, disputes arose over its eastern boundary. Nevada was not established as a separate territory until 1861. Political disagreements and conflicting interpretations of earlier treaties and agreements existed during this period.
- Multiple Surveys: Various individuals and surveyors attempted to establish the boundary, but their surveys often differed. This further complicated matters.
Given these factors, there was much uncertainty and disagreement regarding the California-Nevada boundary in the early years. It was only through the efforts of surveyors like Alexey von Schmidt and subsequent legal and political resolutions that the boundary was eventually clarified and accepted. Von Schmidt’s survey work played a crucial role in resolving these disputes and establishing a more accurate boundary line.
Aurora
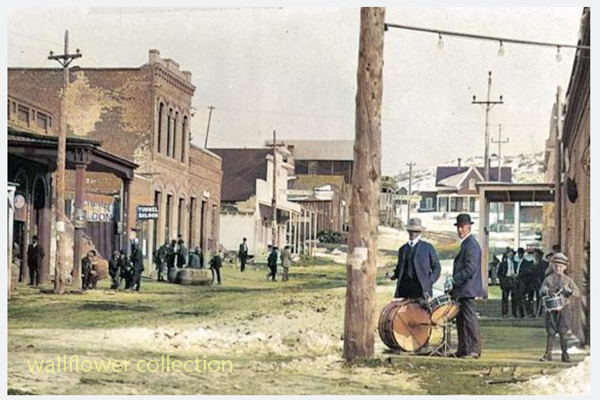

The town of Aurora, Nevada, experienced a move due in part to the boundary disputes between California and Nevada. Aurora was originally founded in the 1860s during the Nevada Silver Rush. At its founding, the exact location of the California-Nevada border was still uncertain and subject to disputes.
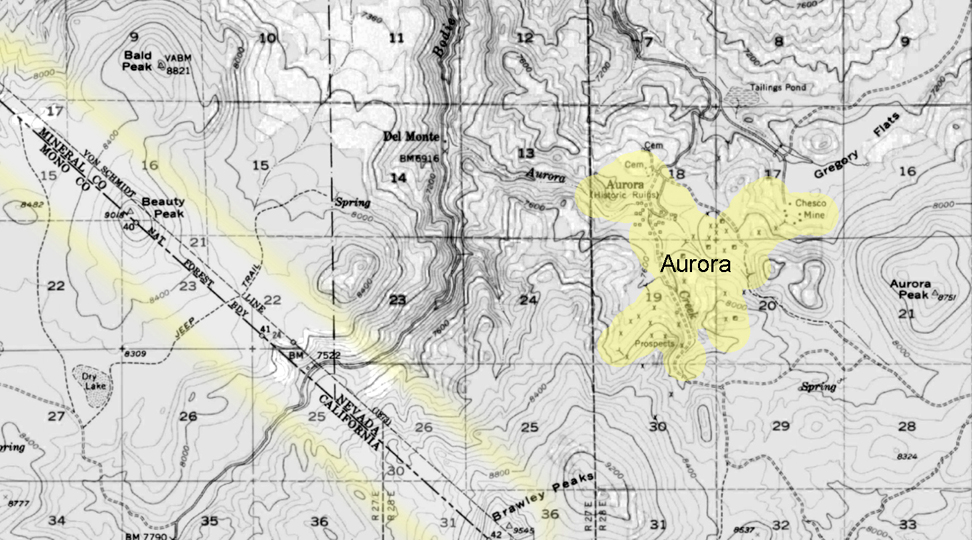
As a result of the boundary disputes and the fact that Aurora’s initial location was close to the border, there were concerns about which state’s jurisdiction the town fell under. Aurora’s residents and businesses moved the town slightly to the east, further into Nevada’s territory, to avoid potential legal and tax issues. This move ensured that Aurora would be firmly within the boundaries of Nevada when the border dispute was eventually resolved.
The relocation of Aurora was a strategic decision made to secure the town’s status as part of Nevada rather than California, given the uncertainties and conflicts related to the state boundary at the time. This move allowed Aurora to thrive as a mining town in Nevada without the legal complications associated with straddling the border.
Is everybody happy?
It’s difficult to determine whether “everybody” is happy, as people’s feelings and satisfaction with their circumstances can vary widely. Happiness is subjective and depends on individual experiences, perspectives, and circumstances.
In the context of the town of Aurora’s relocation due to boundary disputes, it’s possible that the decision to move was made to address specific legal and jurisdictional concerns at the time. The move may have been necessary for the town’s continued growth and prosperity. However, whether every resident or stakeholder was happy with the decision would depend on their perspectives and interests.
In any community or population, there will be a range of opinions and emotions regarding significant decisions like a town’s relocation. Some may have been happy with the move because it resolved legal uncertainties, while others may have been less pleased due to the disruption and changes associated with relocation.
To determine the current happiness or satisfaction of people in a specific context, it would be necessary to conduct surveys or interviews to gather their perspectives and opinions.