/marl-springs/
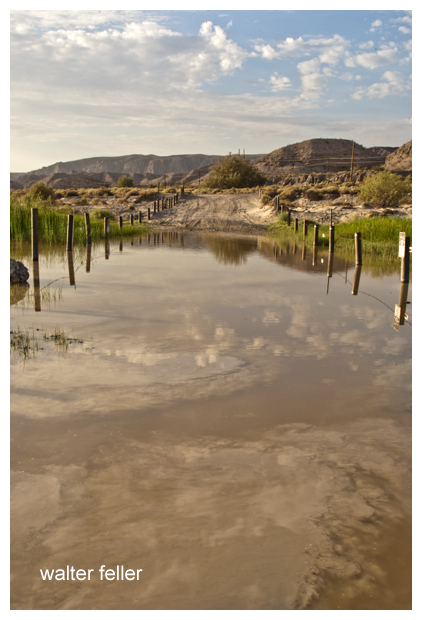
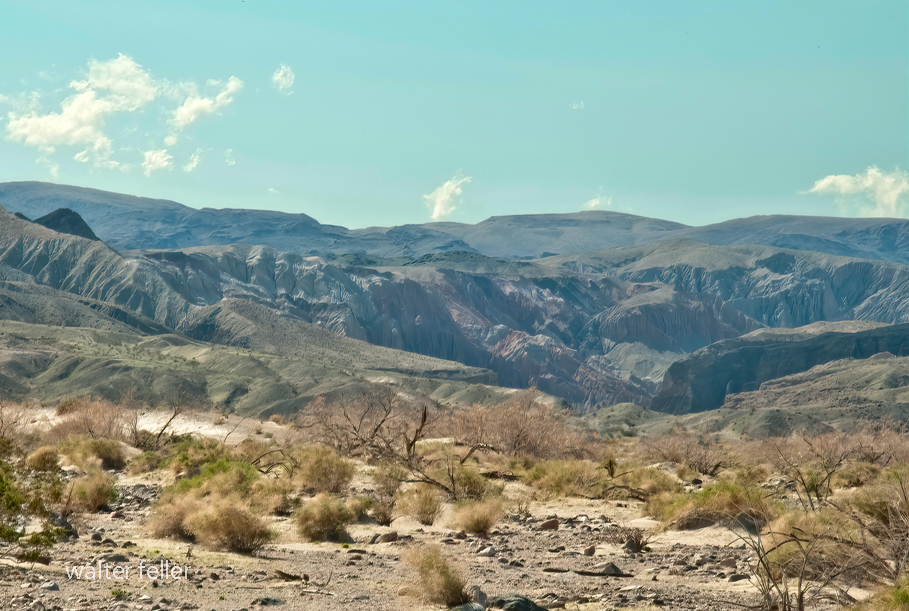
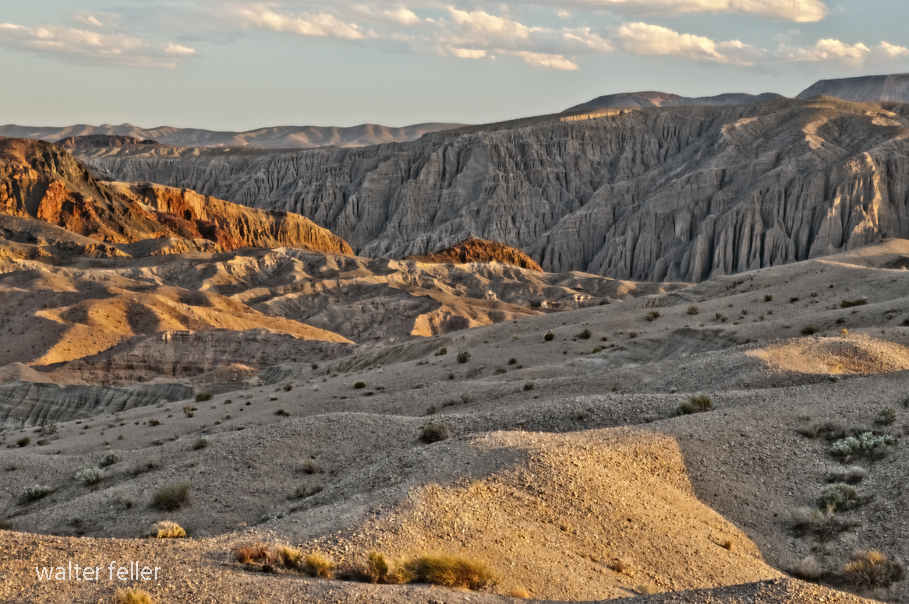
Marl Springs is a historical site located in the Mojave Desert National Preserve in California. The area has significance due to its role as a water source for travelers and settlers in the desert region. Here’s a brief history of Marl Springs:
- Native American Presence: The Mojave Desert has a long history of Native American habitation. The Chemehuevi and Mojave people were among the indigenous groups living in the area. These Native American communities deeply understood the desert environment and its resources.
- Exploration and Early Settlement: In the 19th century, the Mojave Desert attracted explorers, pioneers, and prospectors seeking new opportunities. The Mojave Road, a route through the Mojave Desert, and Marl Springs became a crucial water source for travelers along this route.
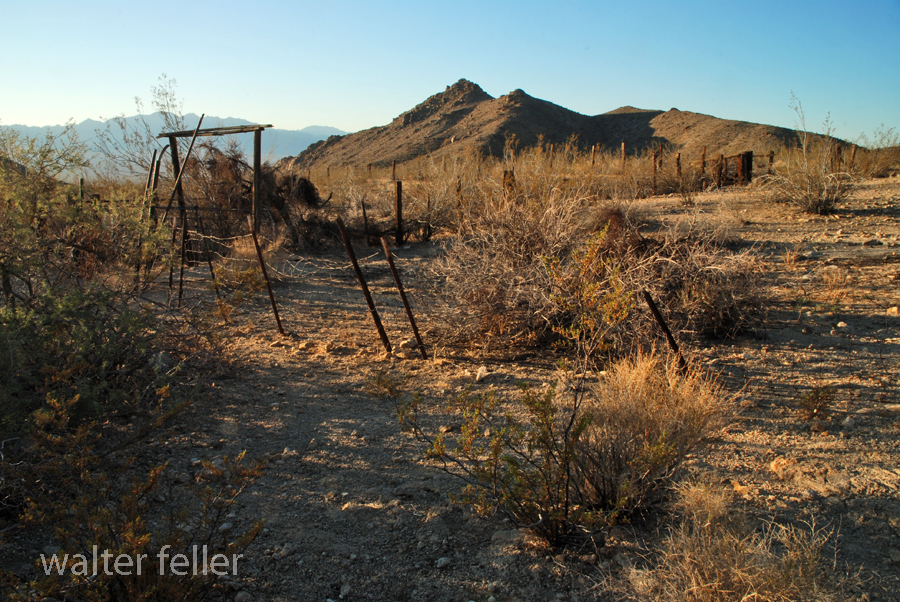
- Military Use: During the mid-1800s, the U.S. Army established a military presence in the Mojave Desert. With its reliable water source, Marl Springs was a strategic location for military operations and a resting point for troops moving through the region.
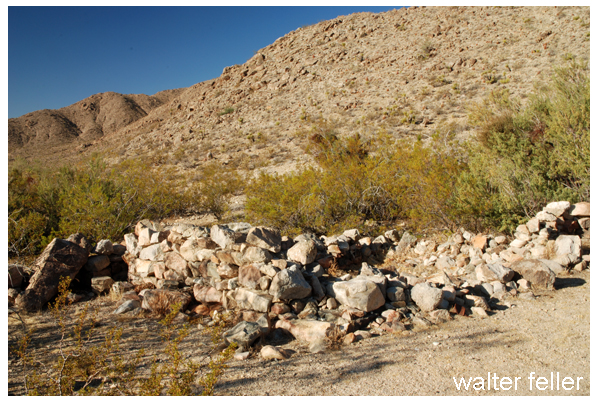
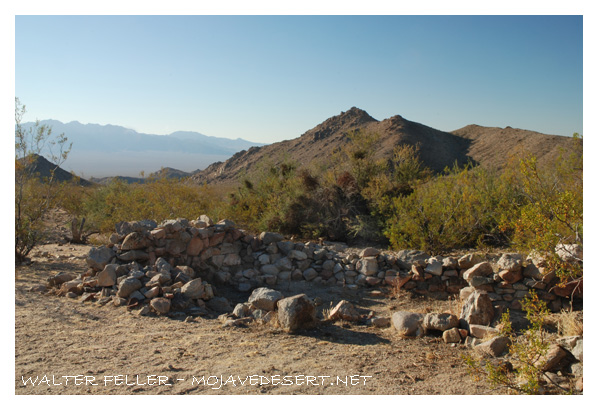
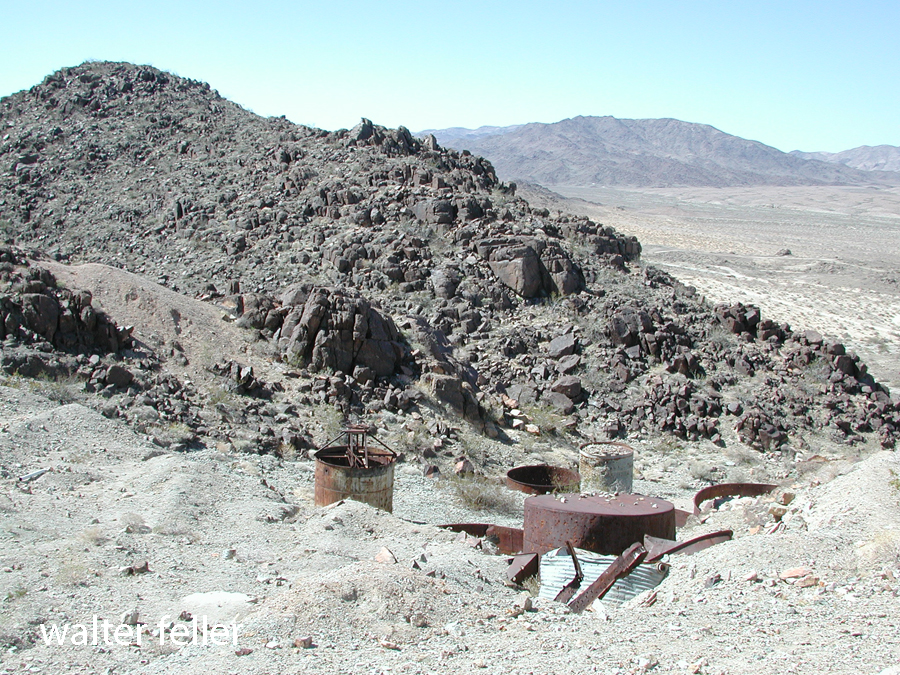
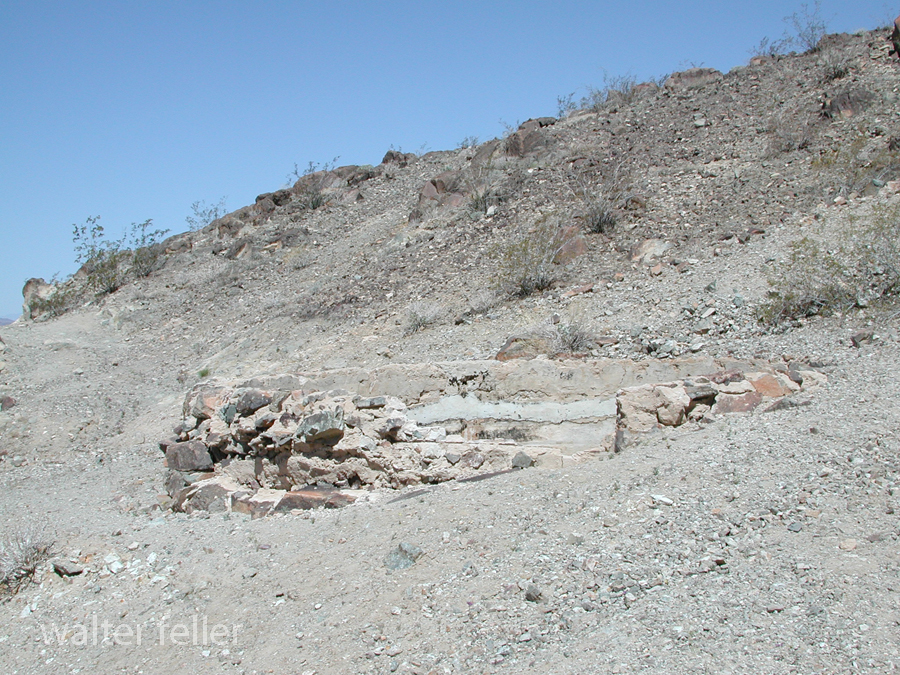
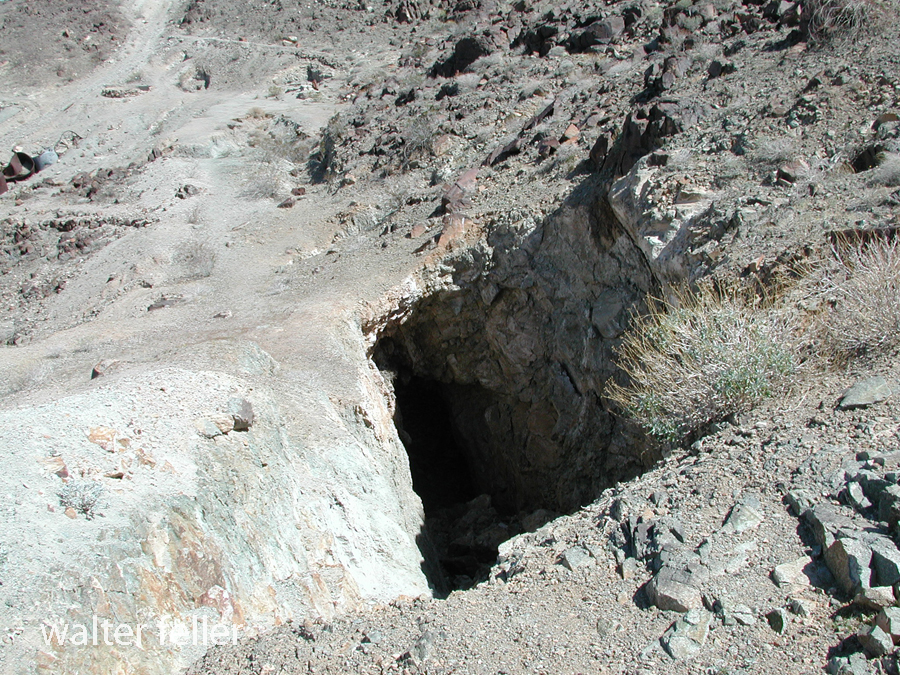
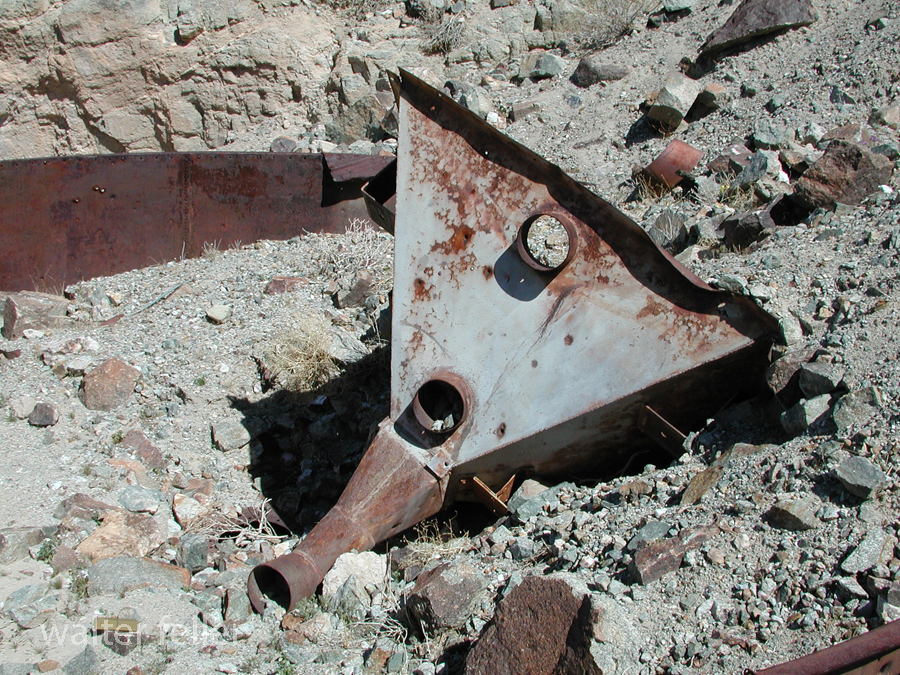
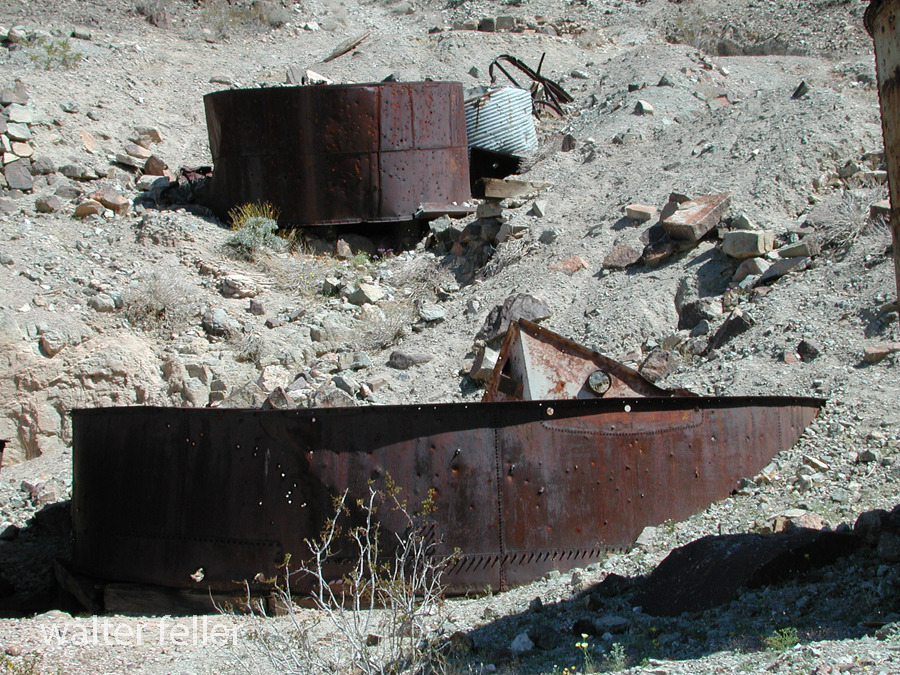
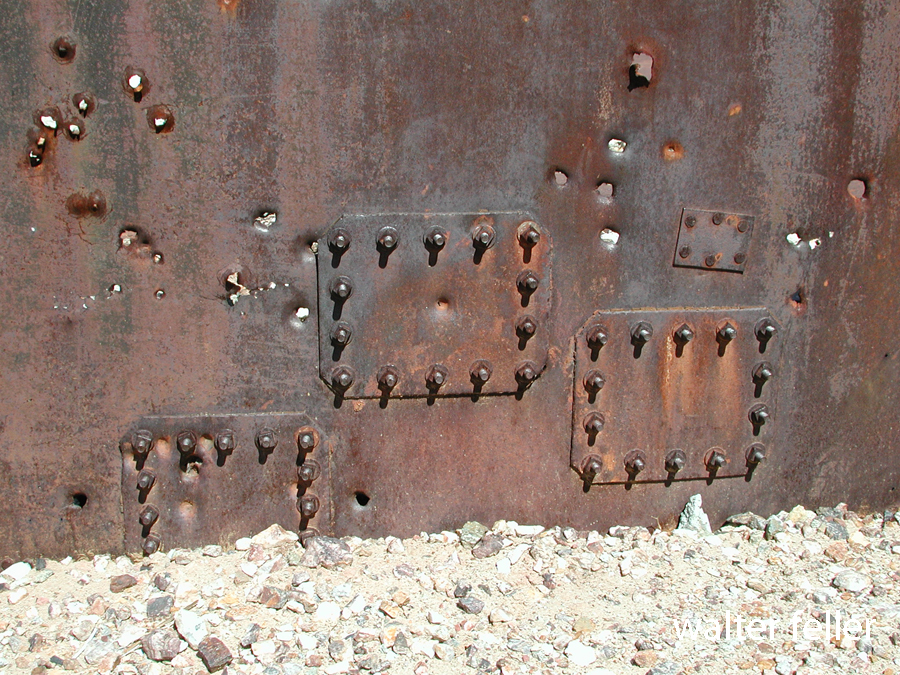
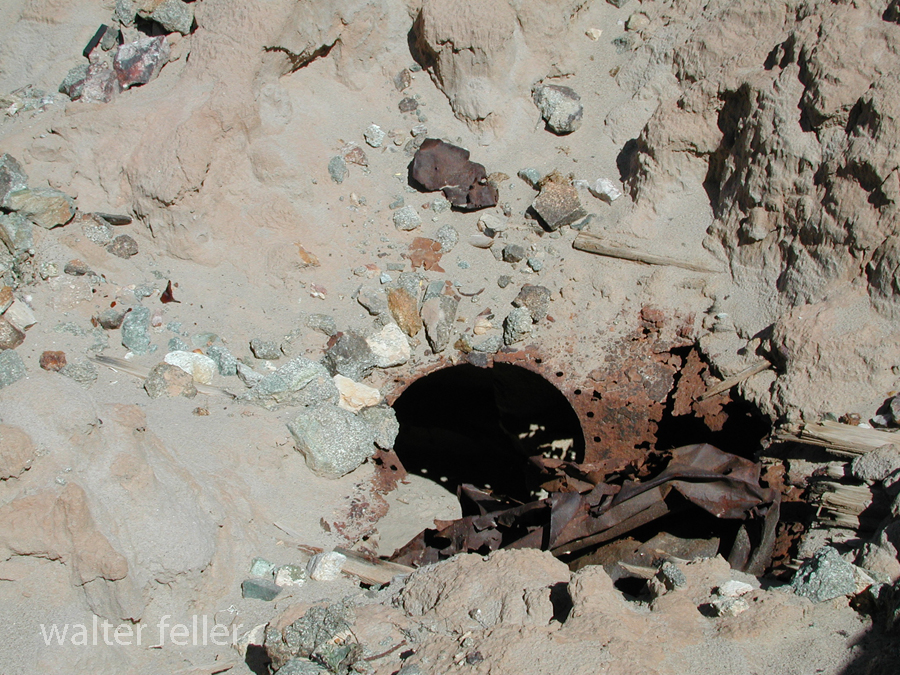
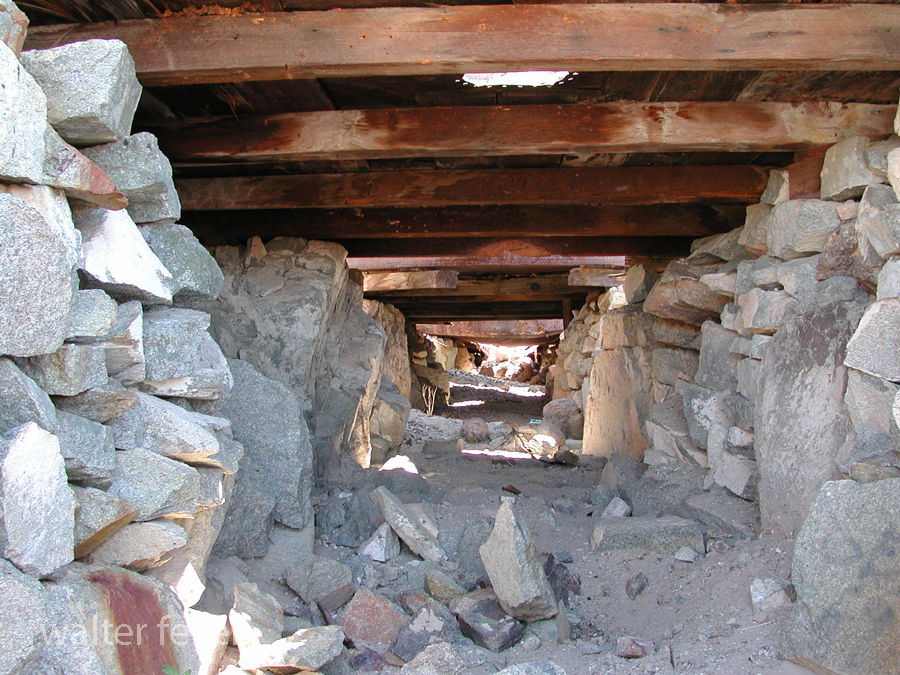
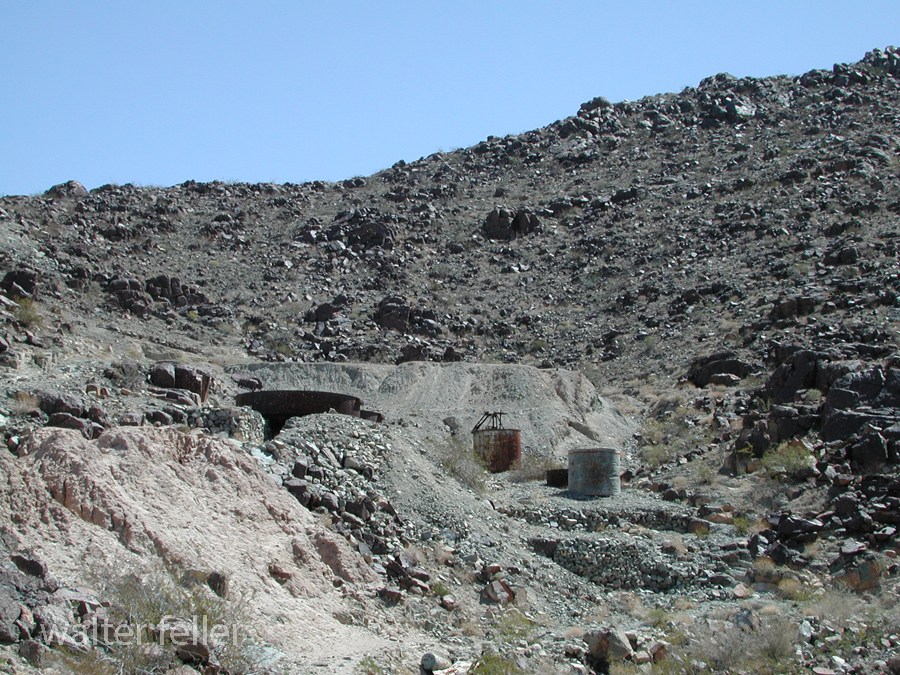
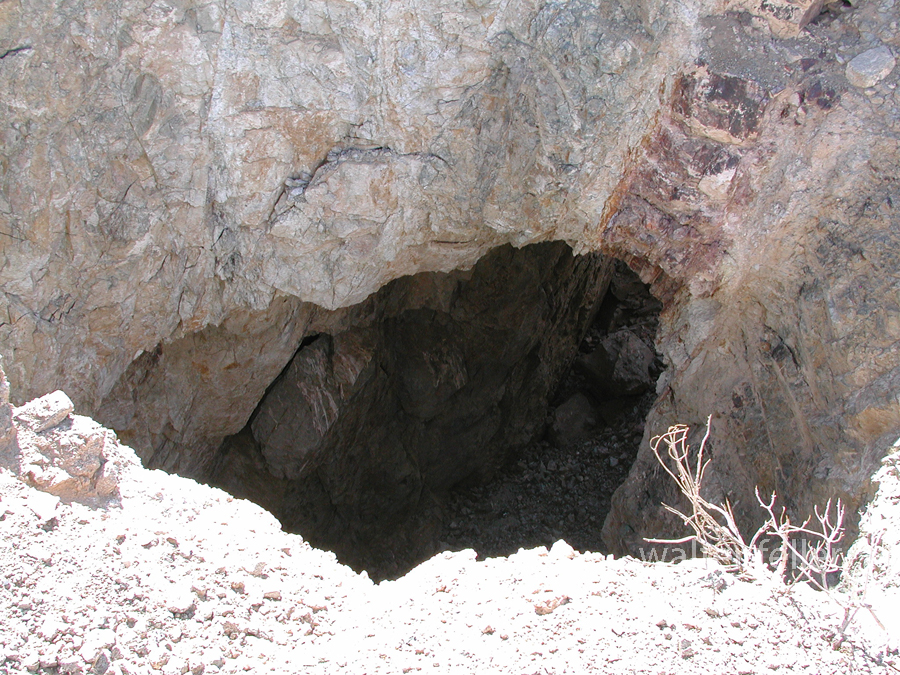
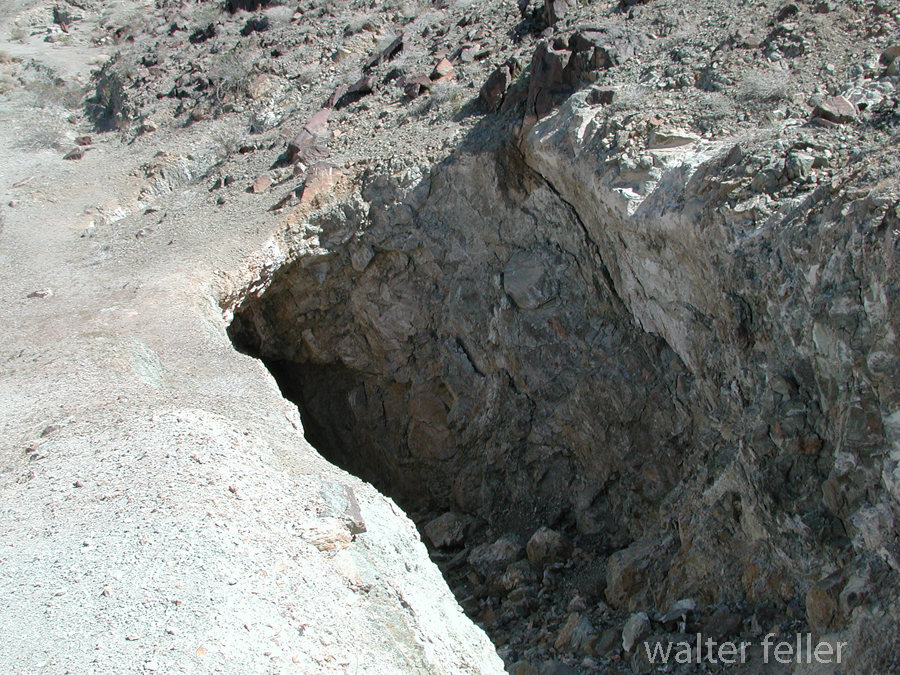
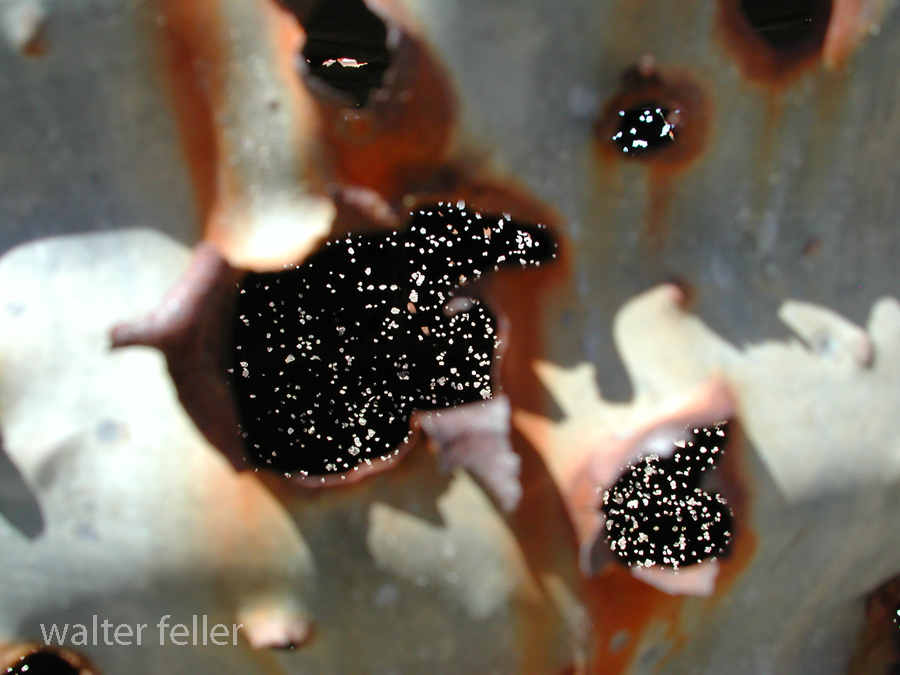
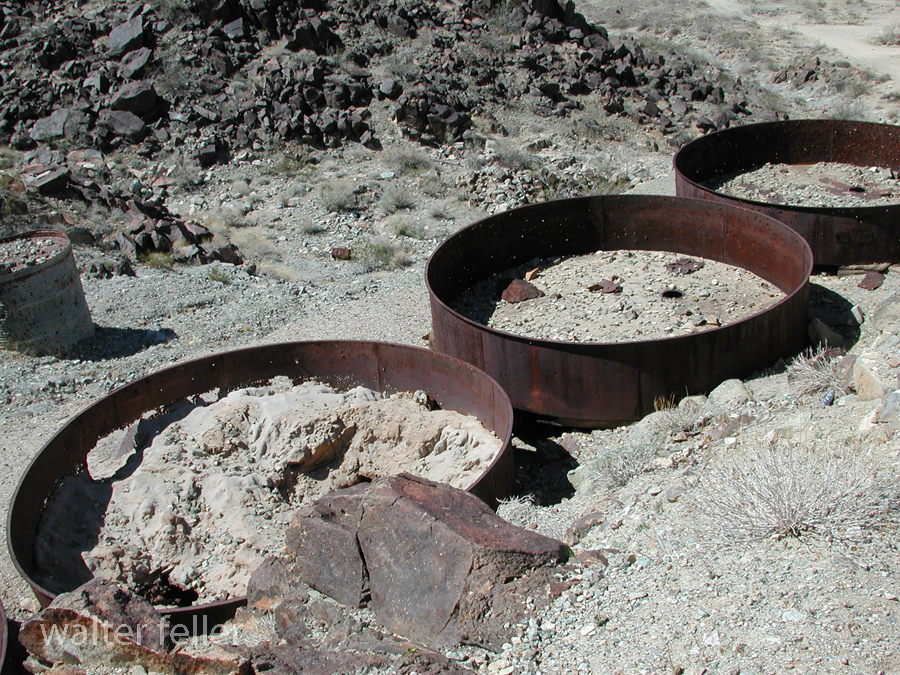
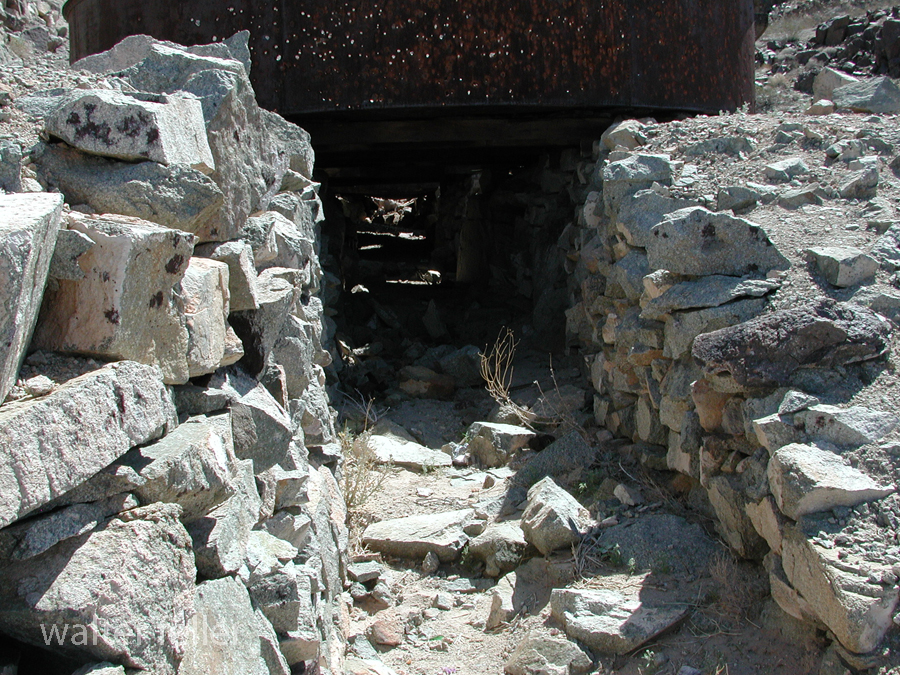
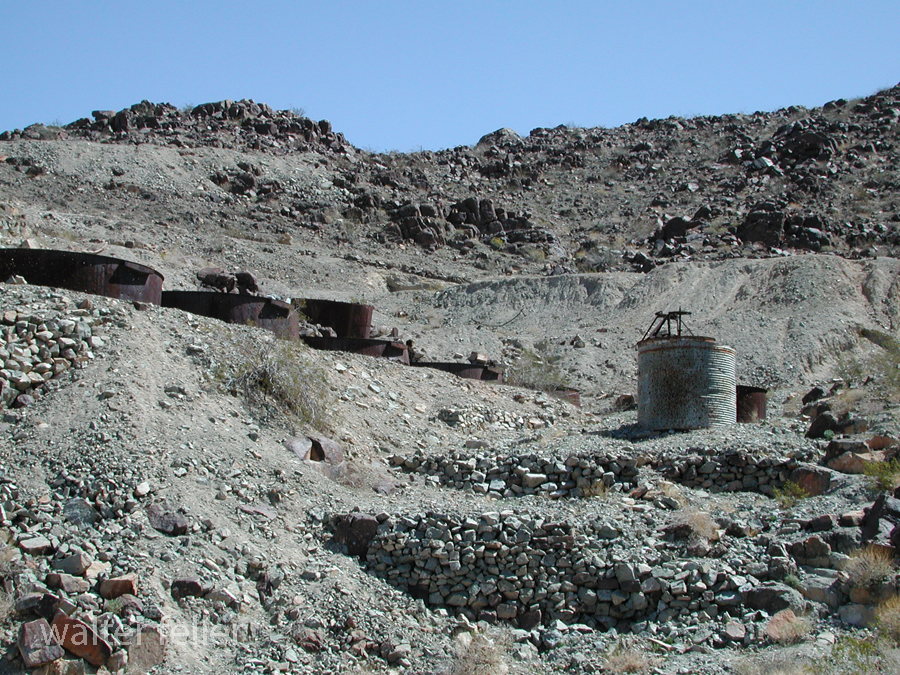
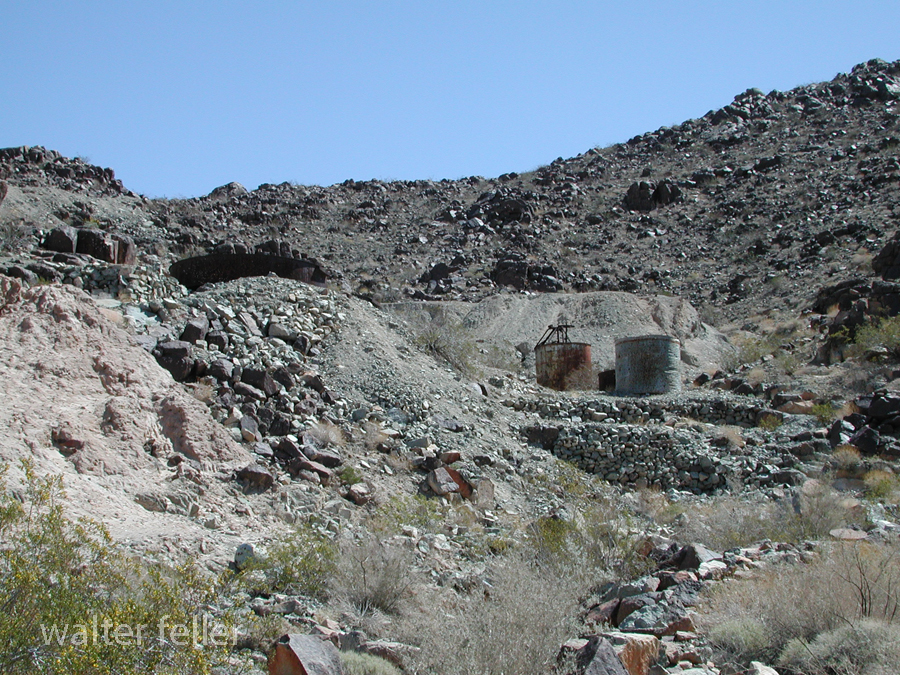
- Mining Activity: Like many areas in the Mojave Desert, Marl Springs saw mining activity during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Prospectors sought minerals such as gold and silver in the surrounding hills, contributing to the region’s development.
- Railroad Expansion: The railroad‘s arrival led to changes in transportation patterns, reducing the importance of some stagecoach routes. However, Marl Springs retained significance for those traveling by road or seeking water in the desert.
- Mojave Desert National Preserve: In 1994, the preserve was established to protect the unique desert ecosystem and preserve its cultural and historical resources. Marl Springs is now part of this national preserve, allowing visitors to explore its historical remnants and appreciate its role in the region’s past.
Today, Marl Springs stands as a testament to the challenges and opportunities the Mojave Desert presents, showcasing the intersection of natural resources, human history, and the development of transportation routes in the American West.