The First Information Highway
Across the Mojave Desert, distance has always been the central challenge, fundamentally shaping the region’s social and economic development. Before the introduction of the telegraph and other forms of rapid communication, travelers, soldiers, and traders moved slowly between scattered springs, river crossings, and mountain passes. Messages traveled only as fast as the horses or wagons carrying them. In this landscape, information lagged behind events, leaving settlements, mining camps, and transportation routes isolated for days. This persistent isolation highlights the importance of the telegraph’s arrival. In this essay, I will examine how the emergence and spread of the telegraph transformed communication in the Mojave, tracing its gradual development, its integration into the transportation and mining infrastructure, and its broader role in connecting the region to the economic and administrative systems of the American West.
The telegraph’s arrival in the nineteenth century transformed communication in the Mojave. As wires were laid alongside railroads and travel routes, the region’s first network emerged—turning settlements and stations into nodes that instantly transported news, business, and personal messages across vast distances. In this way, the once-remote Mojave became part of a coordinated economic and transportation landscape.
The telegraph lines were more than a technological milestone—they turned the desert’s corridors into channels for movement and information, connecting towns from Needles to Barstow and Mojave as part of a regional network.
To understand this transformation, note that the telegraph’s spread across the Mojave was not a single event but a gradual process spanning several decades. Initially, communication lines traced existing corridors: first, military roads in the mid-nineteenth century; then stage routes; and finally, most decisively, railroads beginning in the 1870s. With each advance, as the wire reached new parts of the Mojave, the effective distance shrank. Consequently, remote stations, mining camps, depots, and river crossings could now report conditions, request supplies, transmit orders, and relay market news in near real time.
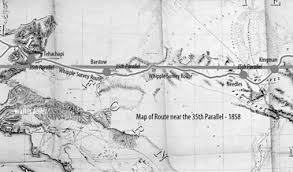
Before the telegraph—throughout the early to mid-1800s—communication across the Mojave depended entirely on physical travel. Messages were moved by rider, wagon, stage, or military courier over routes such as the Mojave Road and the Salt Lake Road. Later in the century, they traveled along the wagon corridors tied to San Bernardino, Fort Mojave, and the Colorado River crossings. As a result, delay, uncertainty, and isolation were the norm. For example, a storm, a washout, a hostile encounter, or a shortage of animals could disrupt message delivery for days. In a region where water, distance, and timing mattered, that limitation was severe.
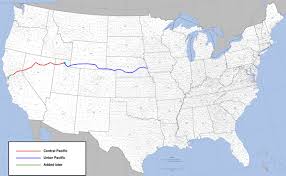
In 1861, the construction of the first transcontinental telegraph line marked a major turning point in American communications, but this initial line bypassed the Mojave. Only after the Civil War, as settlement, military use, mining, and rail transport expanded in the region during the late 1860s and 1870s, did the Mojave begin to develop its own telegraph lines. (Editors, 2009) In the desert Southwest, telegraph lines thrived where regular travel and economic support made maintenance feasible.
Against this backdrop, by the 1870s and 1880s, railroads became the main builders of telegraph infrastructure in the Mojave. As tracks crossed the desert, telegraph poles inevitably followed, since the railroad needed wire as much as rails. To dispatch trains efficiently over long single-track stretches, rapid communication between stations, sidings, yards, and division points became vital. In this way, telegraph offices at depots and section stations became the desert railroad’s nervous system, turning what was once open distance into a managed corridor.
This approach was exemplified by the Southern Pacific’s advance into the greater Mojave in the 1870s. Rail stations were not just stops for passengers and freight; they were communication nodes. A station agent might also serve as a telegraph operator, sending orders, reporting shipments, relaying delays, and linking local businesses to regional markets. Settlements with rail stops often gained telegraphic relevance as well.
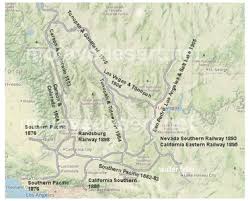
The Mojave corridor’s transformation accelerated in 1883, when the Atlantic & Pacific Railroad—later controlled by Santa Fe—completed its line from Needles to Mojave. This milestone marked a decisive moment in regional communication (Atlantic and Pacific Railroad records, 1889-1893, n.d.). With the railroad came a continuous telegraph, linking Colorado River gateways, desert sidings, supply hubs, and western connections. As a result, towns such as Needles, Fenner, Cadiz, Ludlow, Barstow, and Mojave gained new significance—they became points in an interconnected network, not just locations on a map.
As a result of these shifts, Barstow’s later importance rested partly on this logic. As lines converged and railroad functions intensified, so did telegraph traffic. Train movements, freight, maintenance orders, livestock, mining output, and commercial messages all depended on the wire. Telegraphy made Barstow a control point, not just a stopover. The same applied, more modestly, to smaller stations, whose importance stemmed from siding capacity, water supply, or As the route developed into a major rail corridor after 1901, its telegraph infrastructure expanded, and places such as Daggett and the line toward Las Vegas became part of a communications spine linking Southern California with the Great Basin and the interior West (Guide to the San Pedro, Los Angeles & Salt Lake Railroad Company Records, 2024). In turn, the wire made the entire corridor legible to managers, dispatchers, and officials.
As rail and telegraph lines expanded, mining districts also benefited, though typically only indirectly at first. Mines needed access to a telegraph office, whether at their own camp, a nearby rail station, or a supply town—not a full regional grid. In the Mojave, camps often rose and fell too quickly for elaborate infrastructure, but more durable districts spread communication from the railheads. As one mining superintendent observed in an 1882 report, “With the wire to hand, news of strikes or shipments is sent in minutes, not weeks.” Telegraphy enabled ore buyers, investors, freighters, smelters, and operators to coordinate activities far faster than before. The telegraph was an economic multiplier; however, it did not create mineral wealth, but accelerated extraction and speculation.
Beyond its economic impact, the telegraph fundamentally reshaped the exercise of governance in the desert by enabling authorities to coordinate and intervene over long distances far more effectively than before. Sheriffs, military officers, railroad managers, and commercial entities gained the ability to transmit orders, directives, and requests for aid almost instantaneously, enabling more proactive, coordinated responses to emergencies and routine matters alike. The telegraph enabled the rapid management of crises such as accidents, conflicts, floods, labor disputes, supply shortages, and equipment failures. In a region where low population density and vast expanses had previously hindered centralized oversight and delayed administrative actions, the telegraph facilitated more timely decision-making and remote supervision. In effect, telegraphy became not just a technical advance but a core administrative instrument that altered patterns of authority and governance in the Mojave Desert. (Schwoch, n.d.)
Socially, the telegraph drew isolated desert communities into a broader world, fostering new cultural connections and a sense of participation in national affairs. Telegraph offices not only provided access to newspapers, commodity prices, railroad schedules, political news, and personal messages, but also exposed residents to broader currents of information and social change. The resulting increase in awareness allowed Mojave inhabitants to engage more actively with markets, politics, and news beyond their immediate environment. However, it is important to recognize that these benefits were not experienced equally by all residents. Some individuals and communities, particularly those unable to afford telegraph services or lacking easy access to the wire, may have found themselves left further behind as information and economic opportunities flowed to more connected settlements. Although expensive and specialized compared to mail, the telegraph’s symbolic value was enormous, representing technological progress and integration with modern society. (Schwoch, 2019) Nevertheless, while a desert station with a telegraph key was no longer truly remote, those without such infrastructure could remain marginalized—demonstrating that technological advancement could both connect and divide communities within the Mojave. In this sense, the telegraph’s integration sometimes reinforced social and economic disparities, complicating the narrative of universal connectedness and belonging to the broader American experience.
By the early twentieth century, telegraph service across the Mojave had become routine but remained crucial. It laid the groundwork for later advances like telephones and radio, proving that main corridors were channels of information as significant as the rails.
The development of the telegraph across the Mojave can be divided into three clearly defined stages. The first stage, prior to the 1860s, was characterized by a pre-wire desert that relied entirely on courier communication, with messages delivered by riders or wagons. The second stage, spanning the mid to late nineteenth century, marked a transition, as growing military, commercial, and transportation demands increased the need for more rapid communication, prompting the initial spread of telegraph lines along established routes. The third stage began in the 1870s and extended into the early 1900s, when the expansion of railroads led to the widespread installation of telegraph lines along the main transportation corridors of the desert, making telegraphic communication a standard feature of the Mojave (Axotl, 2025). While the telegraph did not conquer the Mojave by itself, its expansion demonstrated a new order: the desert was transformed from a space merely traversed into one constantly monitored, coordinated, and integrated.
By the early twentieth century, telegraph offices at railroad depots relayed train orders and freight movements, connecting desert settlements with distant cities and enabling coordination with markets and administrative centers beyond the desert.
Although later technologies—such as the telephone, radio, and digital communication—replaced the telegraph’s practical role, it is important to remember that the system it created marked a turning point in the region’s history. The telegraph bound the Mojave Desert into the economic and administrative framework of the American West and enabled information to travel as quickly as railroads carried people and goods.
Seen in this light, the telegraph poles that once lined the desert rail corridors represented far more than mere infrastructure. They signaled a profound transformation in the region’s social and economic fabric, marking the Mojave’s entry into the networks that shaped the modern American West.
Alongside the development of railroads and roads, the telegraph fundamentally redefined the meaning of distance and isolation in the desert. By enabling near-instantaneous communication, it not only connected settlements but also facilitated new forms of economic coordination, administrative oversight, and social engagement. Ultimately, the arrival of the telegraph was not simply a technological change: it reimagined the Mojave as part of a broader, interconnected world, demonstrating how technological innovations can reshape both the lived experience and future possibilities of even the most remote regions.
—