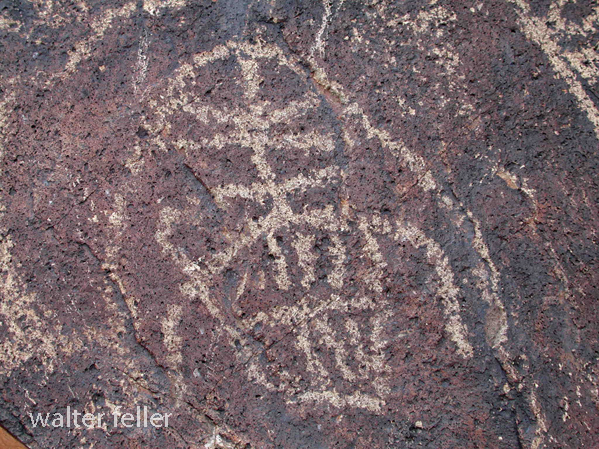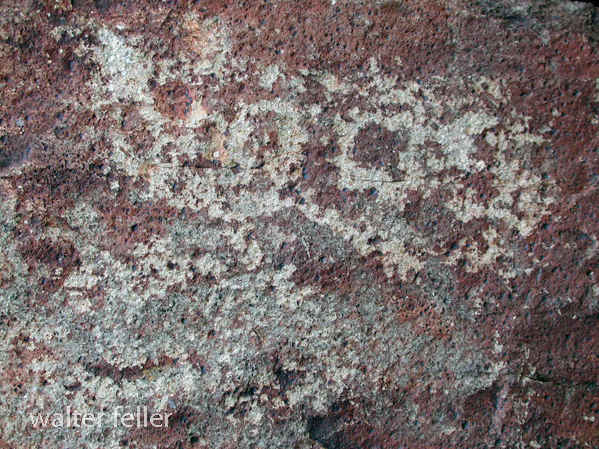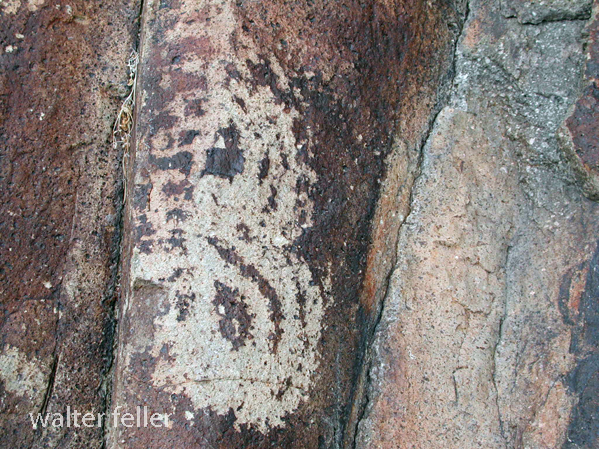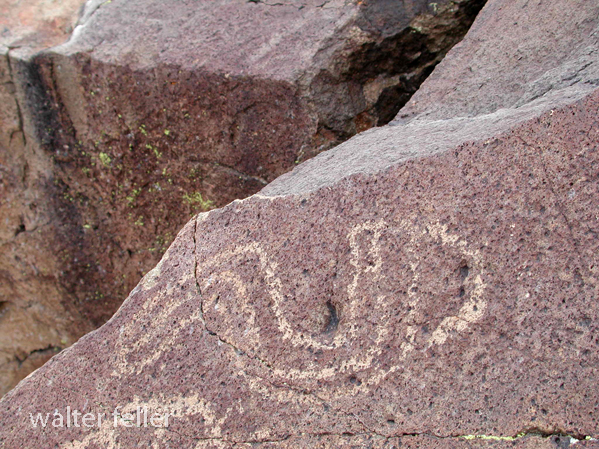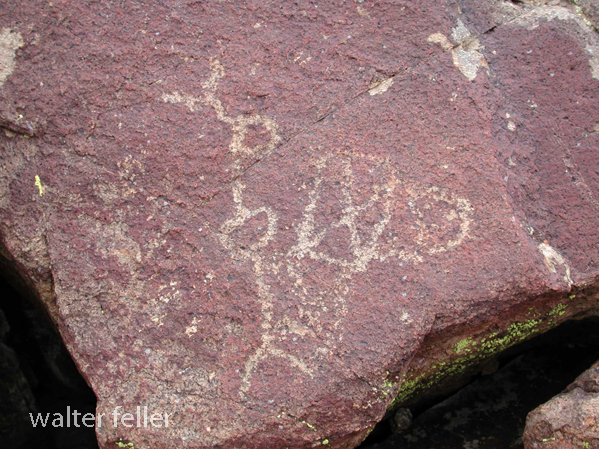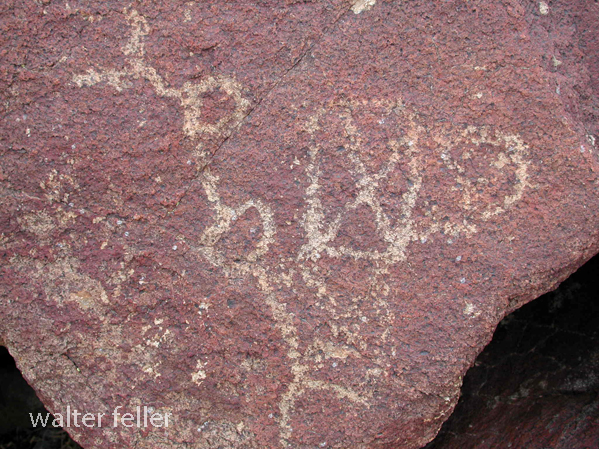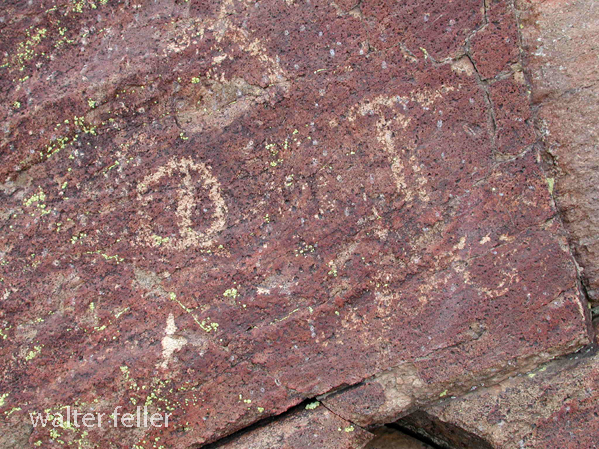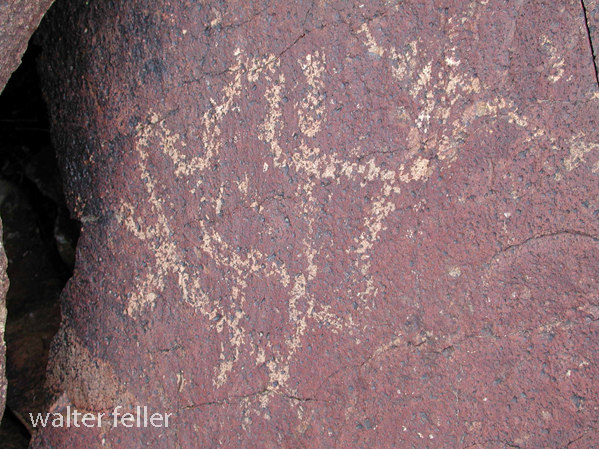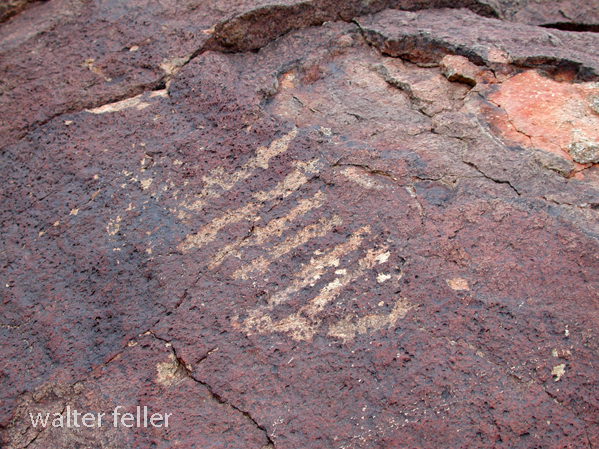/petroglyphs/
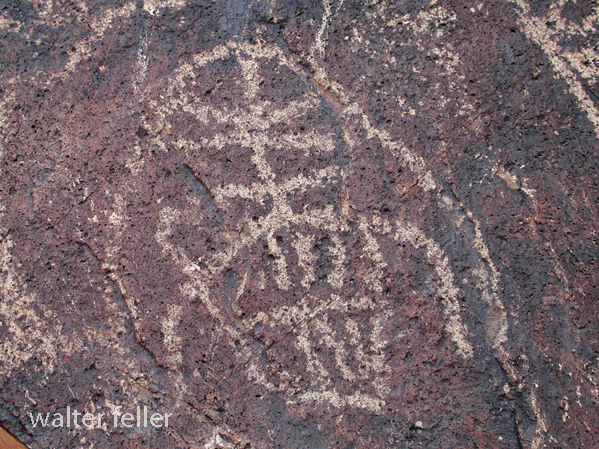
The Mojave Desert, located in the southwestern United States, is rich in cultural and historical significance, with evidence of human habitation dating back thousands of years. Petroglyphs, pictographs, and geoglyphs are among the archaeological features found in the Mojave Desert, offering glimpses into the region’s past.
Here’s a brief overview of each:
- Petroglyphs:
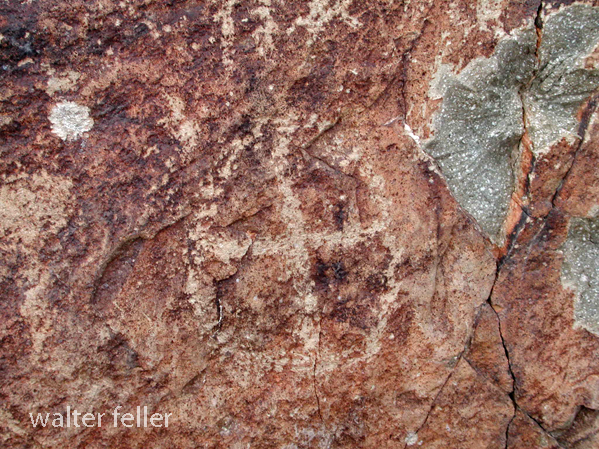
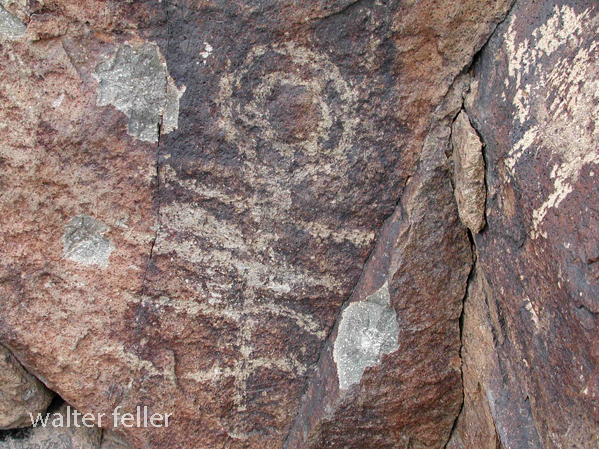
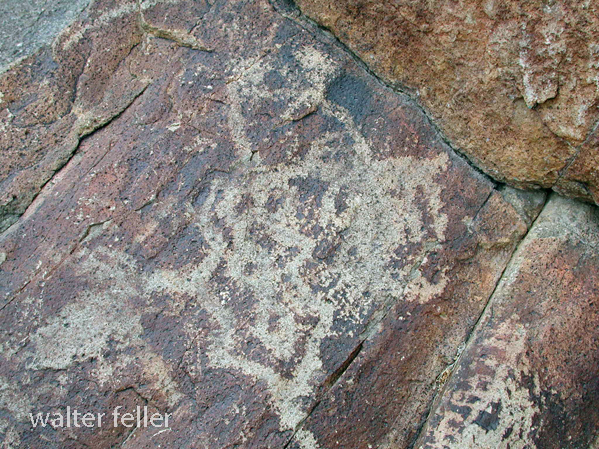
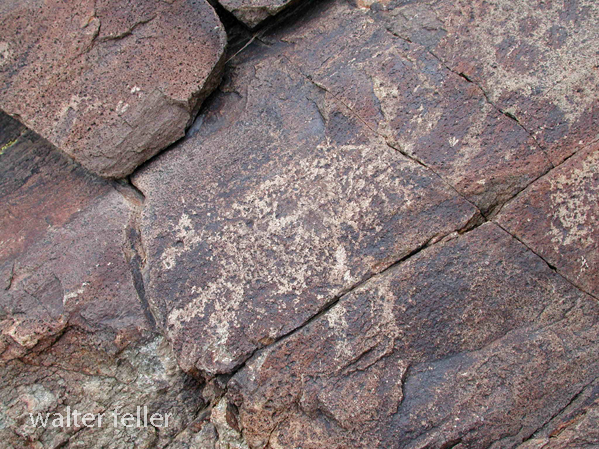
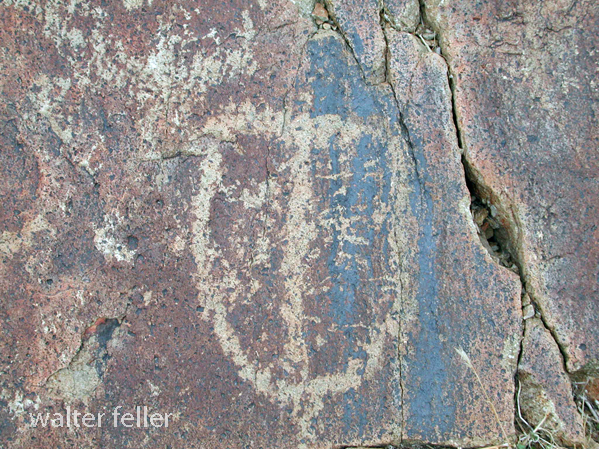
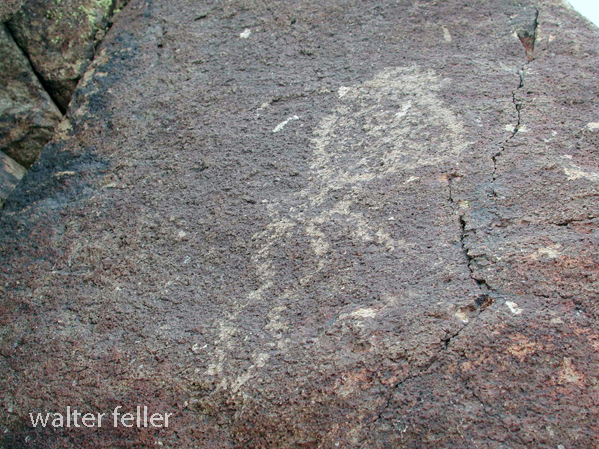
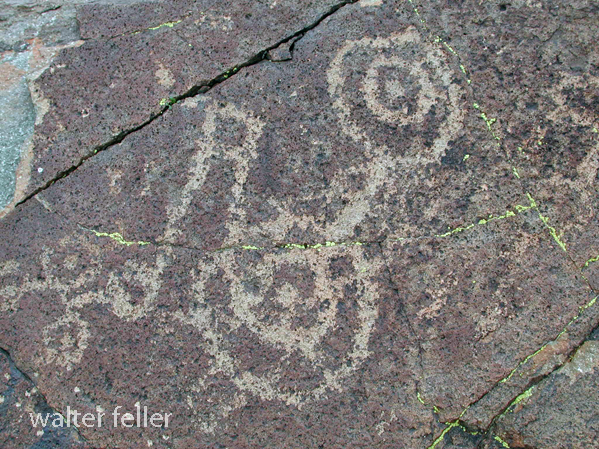
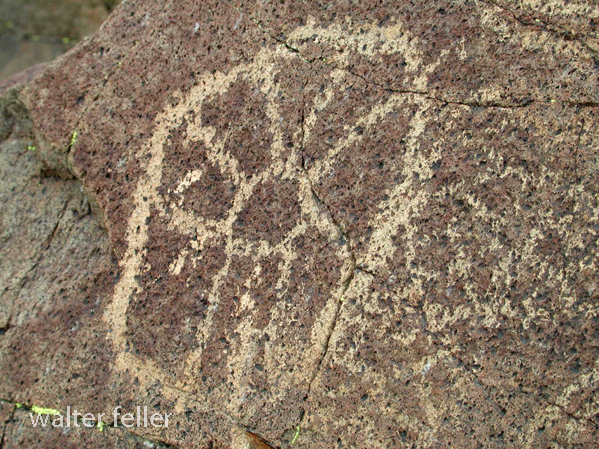
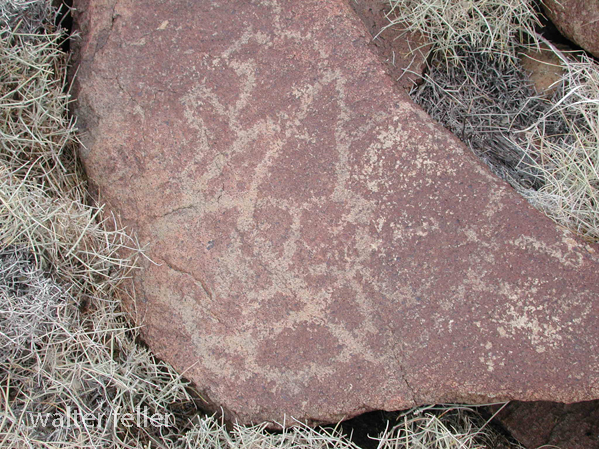
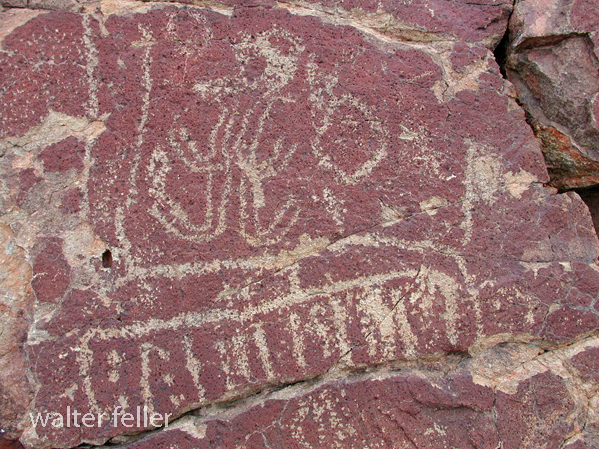
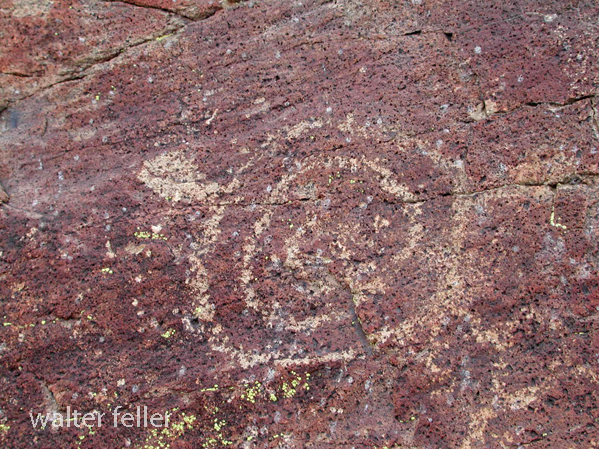
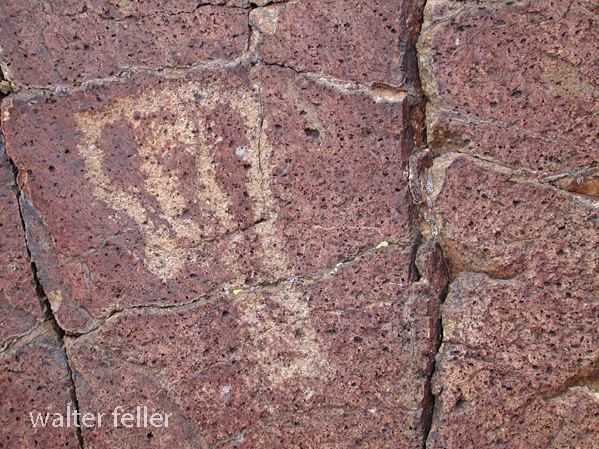
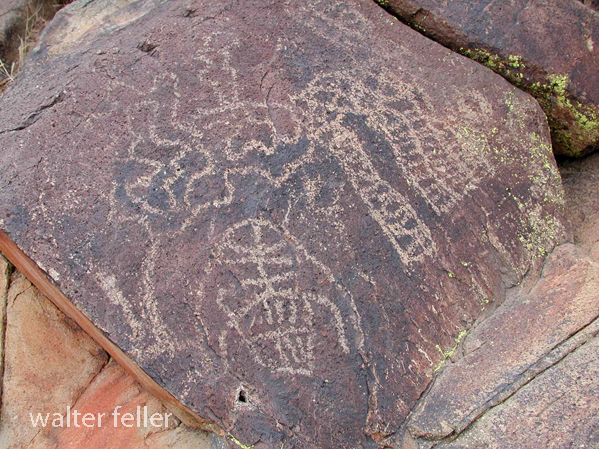
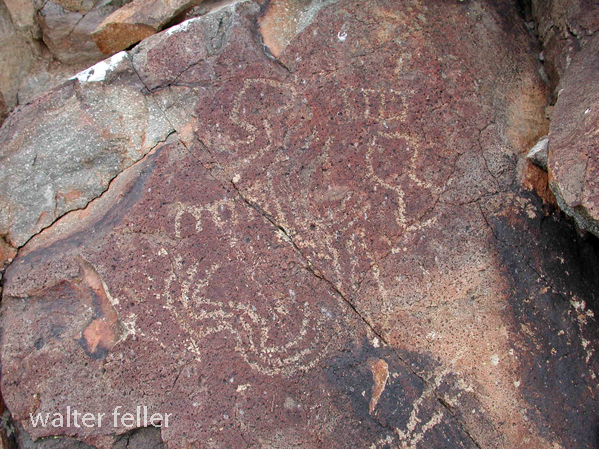
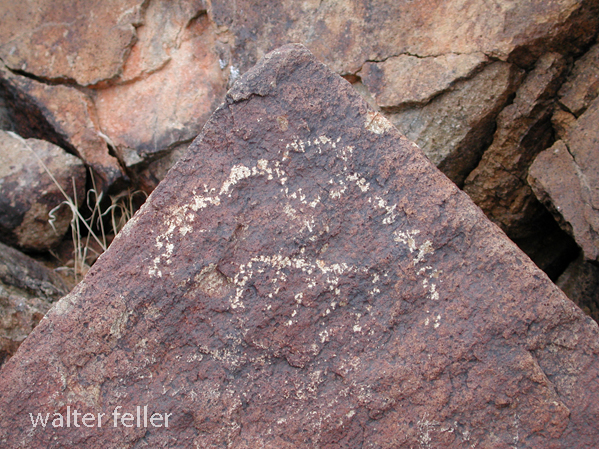
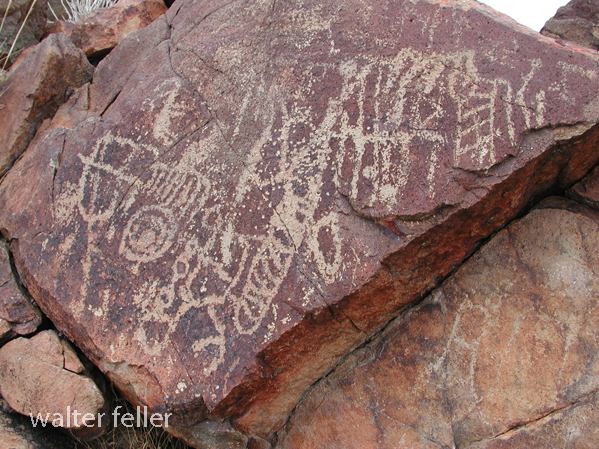
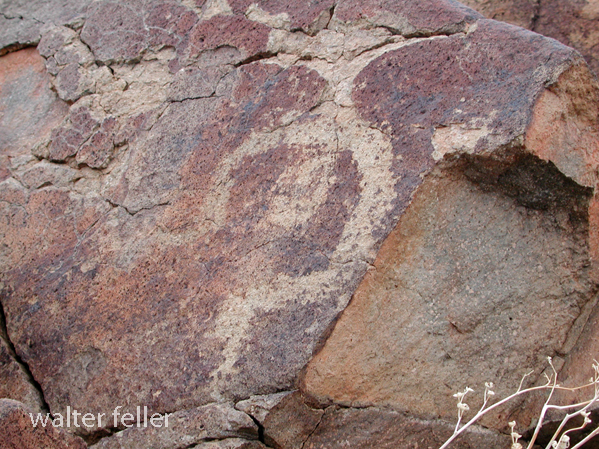
- Petroglyphs are rock engravings created by carving or pecking into the surface of a rock.
- They are often found on exposed rock surfaces, such as canyon walls or large boulders.
- Petroglyphs in the Mojave Desert can depict various symbols, animals, human figures, and abstract designs.
- Native American communities made these carvings as a form of communication, storytelling, or spiritual expression.
- Pictographs:
- Pictographs are rock art created by applying pigments to the surface of rocks. These pigments are usually composed of natural materials like plant extracts or mineral pigments.
- Pictographs are found on rock shelters, caves, and cliff faces, often in areas with some protection from the elements.
- Like petroglyphs, pictographs in the Mojave Desert can represent various subjects, including humans, animals, and symbolic patterns.
- The pictograph colors can include red, black, white, and yellow, with red being a common choice.
- Geoglyphs:
- Geoglyphs are large designs or motifs created on the ground’s surface, often by arranging stones or altering the landscape’s natural features.
- While geoglyphs are more commonly associated with other regions like the Nazca Lines in Peru, there are examples of geoglyphs in the Mojave Desert as well.
- The Blythe Intaglios, located in the lower Colorado River valley near Blythe, California, is a notable example of geoglyphs in the Mojave Desert. These large human and animal figures were created by scraping away dark rocks to reveal the lighter soil beneath.
Preservation of these cultural artifacts is crucial, and many sites are protected to prevent vandalism and degradation. Researchers and archaeologists work to study and document these features, shedding light on the history and practices of the indigenous peoples who lived in the Mojave Desert. It is important visitors respect and avoid disturbing these archaeological sites to ensure their preservation for future generations.