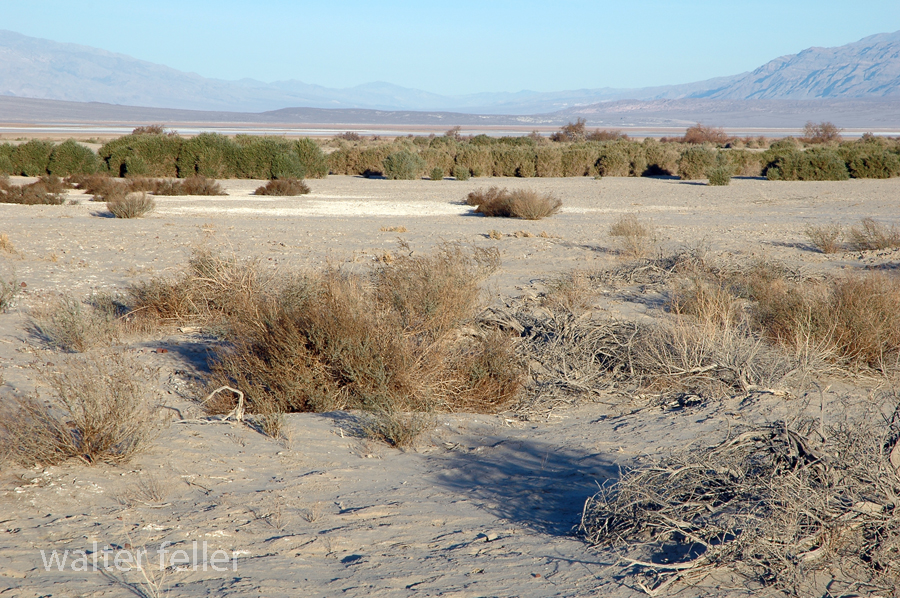
In 1849, a wagon train bound for California split up, with many members opting for a supposed shortcut to the goldfields. The shortcut did not work out, and these intrepid wanderers found themselves stranded, lock, stock, barrel, and four children on the floor of a place called ‘Death Valley.’

Over a month of hardship and waiting had passed while two heroic young men walked to find a way out and return with supplies to bring this band of Lost 49ers to safety. This they did, returning with food, a white horse, and a one-eyed mule. Sadly enough, the white horse had to be abandoned in a dry fall in the Panamint Mountains.
With these heroes returning, they could make their escape. The children were weak, tired, and sick and would not make the trip if they had to walk, so the pioneers sewed several shirts together, making saddlebags to carry them in.

The children were uncomfortable and sick. They cried, but ‘Crump,’ the ox selected to bear this burden, seemed to sense the importance of carrying its cargo as gently as possible, never missing a step, stumbling, or even making a sudden, jarring move.
This ordeal, beginning late in 1849 and finishing up early in 1850, became a distant memory to the party members.

Years later, a much older William Manly, one of the two heroes who saved the emigrants (John Rogers being the other), was walking down a road in the Central Valley. He noticed that over in a shady pasture, there was a fat ox relishing the long, tender blades of grass. Strangely enough, the ox looked vaguely familiar. Sure enough, it was Old Crump, warm and gentle as ever.
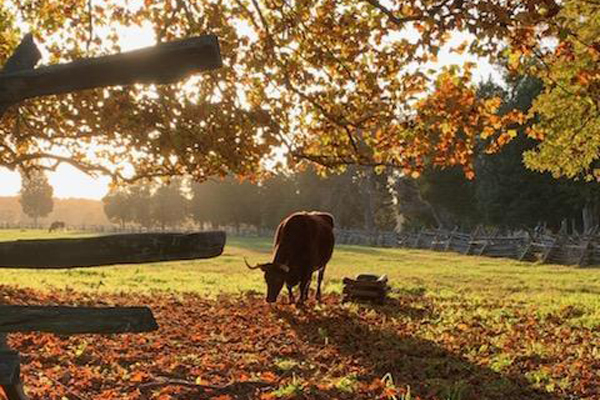

Back in 1850, when things settled after their hardship-fraught journey and arrival at their destination, the owner of the ox retired the creature as a reward for its distinguished service, and Crump never worked another day in his life.
Chapter XI – Death Valley in 49
Wm. Lewis Manly