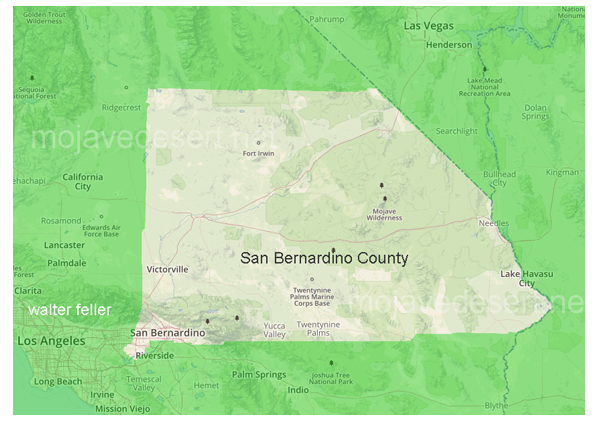
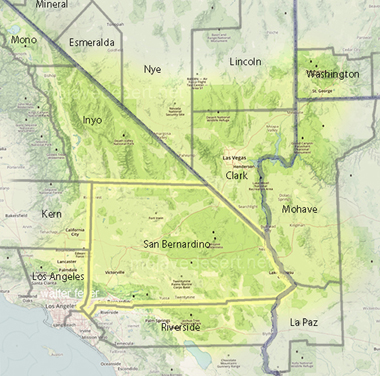
San Bernardino County
Timeline
This timeline is not all inclusive of the county's historical events--only those related in one way or another to the Mojave. - Editor1853
In April, the state legislature creates the County of San Bernardino from what was formerly Los Angeles County.
The first Court of Session creates three townships: San Bernardino, San Salvador, and Chino.
County schools have a total enrollment of 263 children.
1854
Isaac Slover, one of the original settlers of Politana in 1844 (1842?), is killed by a bear somewhere near present-day Wrightwood.
The City of San Bernardino is incorporated as the county seat. Amasa Lyman is elected mayor.
John Brown Jr. discovers gold in Bear Valley.
1855
The county has seven schools and 651 pupils.
Two camels belonging to the U.S. Army came through Cajon Pass to San Bernardino en route to Fort Tejon in Los Angeles County.
Mormons are recalled to Salt Lake City from San Bernardino.
1858
Butterfield stage coaches from St. Louis, Missouri, start rolling through San Bernardino County.
The first county building, a jail, is erected.
1858-1860
Military forts at Camp Cady, Soda Lake, Rock Springs, Piute Springs, and along the Colorado River at Fort Mojave are established in the Mojave Desert to protect travelers on the Old Government Road.
1860
L. Mecham brought bees to the county and established a flourishing honey industry.
William F. Holcomb and Ben Ware discovered gold in Holcomb Valley and a gold rush started. The discovery was the largest in southern California. Gold was also discovered in Lytle Creek.
Major Carleton and eight Native American chiefs reach a treaty agreement that ended raids. When the army withdraws from the desert forts during the Civil War, the treaty is broken.
1861
There are 230 voters at the Holcomb Valley precinct: nearly as many as the entire rest of the county combined. A margin of only two votes kept Belleville (in Holcomb Valley) from becoming the county seat.
John Brown Sr. builds a toll road from Devore to Cajon Pass summit.
1862
The Board of Supervisors order that "all persons confined to county jail ... be placed in chain gang with ball and chain and required to labor on public roads in the county."
The Santa Ana River floods, inundating the Agua Mansa area and its settlement of 200 families. Only San Salvador Church and a single home remain standing.
1867
Citizens petition the Board of Supervisors to impose a road poll tax of twenty cents per every able-bodied citizen between ages 21 to 50 (except Indians).
1870
San Bernardino County's population is 3,988.
Ivanpah, in the northeast corner of the county, becomes a major silver-producing district.
1873
The San Bernardino Borax Mining Company is organized on Searles Lake.
Prospectors find rich silver ore in the Panamint Mountains.
1874
Honey from San Bernardino takes first prize at the World's Fair in St. Louis.
1875
Southern Pacific begins operating trains between Los Angeles and Colton.
1878
The Board instructs County Surveyor Fred Perris to cooperate with Inyo County in establishing the boundary between the two counties.
1880
A survey is made for a reservoir site in Big Bear Valley. Work on the dam starts in 1883.
1881
Silver is discovered at Calico, destined to become one of the richest and most famous mining towns in the West.
1882
California Southern Railroad is completed between San Diego and Colton. It did not proceed into San Bernardino because of disagreements between competing railroad companies. It finally crosses the tracks in Colton and reaches
San Bernardino in 1883.
Daggett is named for John Daggett, who was to become the Lt. Governor of California (1883-87).
1884
Borax is discovered in the Calico district. Successful mining includes hauling ore by 20-mule teams.
1885
The first irrigation water from Big Bear Lake comes to Redlands.
The first train of the Southern California Railway (a Santa Fe subsidiary) passes through Cajon Pass, en route from San Bernardino to Barstow.
Marion "Borax" Smith organizes the Pacific Borax Salt and Soda Company. By 1890, Borate in the Calico Mountains is the nation's chief source of borax.
1886
Railroad rate wars start a California population boom.
Needle's first school starts in a wickiup-type structure of poles and adobe. It later moves to a railroad tool house.
1888
Robert Whitney Waterman of San Bernardino becomes Governor of California.
1889
Santa Fe constructs Topock Bridge across the Colorado River at Needles.
1891
California Portland Cement incorporates and begins manufacturing cement at Slover Mountain.
1892
Riverside County is created from San Bernardino and San Diego counties, taking with it Riverside, Corona, Beaumont, and Banning.
1893
President Benjamin Harrison creates the San Bernardino Forest Reserve, which becomes the San Bernardino National Forest in 1907.
1894
San Bernardino declares it is a nuisance to throw scrap iron, glass, nails, or tacks on public streets.
1895
The Yellow Aster gold mine is discovered in Randsburg.
1901
The post office changes the name "Victor" to "Victorville."
1902
The Board of Supervisors amends the 1897 rates for toll roads to include a toll of $25.00 (one way) for automobiles. This was to discourage automobiles as a danger to persons and property on the roads.
The San Bernardino Valley Traction Line begins service.
1904
The Tonopah and Tidewater Railroad is built to Death Valley.
1905
A dam is erected to form Little Bear Lake, now Lake Arrowhead.
1907
The first automobile reaches the crest of the San Bernardino Mountains.
1908
Hinkley gets a school and a post office.
1909
George Hinkley, city engineer of Redlands, paints a line on the street at a dangerous corner with aluminum paint to help guide motorists: this is probably the first "white line" ever used on a roadway.
1910
The first truck reaches the crest of the San Bernardino Mountains, hauling cement for the Lake Arrowhead dam.
1912
California Interstate Telephone Company extends service to San Bernardino County.
Lanfair agricultural center is started in the Mojave Desert; the Lanfair School District is organized in 1913. By 1926 the post office had closed because dry years and opposition from cattle ranchers overcame attempts to farm.
1913
Needles becomes an incorporated city.
Baker records the national high temperature record: 134 degrees F. In the 1990s, Baker constructs the world's tallest thermometer, 134 feet in height.
1914
The Llano del Rio Colony was founded between Victorville and Palmdale. This socialistic agricultural community started with five members and by 1917 had 900.
1916
A steel arch highway bridge is erected at Topock. Celebrations are held in Needles and Kingman.
1917
Southwestern Portland Cement Company opens at Victorville.
1920
David Thompson, a water-supply author with the U.S. Geological Survey, estimates that as many as 100 cars per day use desert roads.
1923
A state highway is built over the top of Big Bear Dam.
1925
The first vineyards are planted in Adelanto.
1933
President Herbert Hoover establishes Death Valley National Monument.
1936
Joshua Tree National Monument is established.
1937
The Asistencia, a recreated outpost of the Mission San Gabriel, opens at the site of the original mission estancia.
1946
Apple Valley opens up to lot buyers.
1947
The City of Barstow is incorporated.
1952
The first meeting of the San Bernardino County Museum Association is held.
1959
The Board of Supervisors declares its intention to establish and maintain a San Bernardino County Museum.
1964
Scientific excavation begins at the Calico Mountains Archaeological Site in Yermo. This "Early Man Site" will gain world-wide attention when Dr. Louis Leakey and the National Geographic Society become involved.
San Bernardino is the site of the first official U.S. concert of The Rolling Stones.
1966
Agua Mansa Pioneer Cemetery in Colton gains protection as a county museum historical site.
1977
The historic Stone Hotel and Peoples General Store in Daggett are acquired by the county for preservation as historic sites. Battles rage over the disposition of the huge "Old Woman Meteorite", found by prospectors near Essex.
2000
The population of San Bernardino County reaches 1.7 million, an increase of 20% over 1990 [2.041 (2010) 2.18 million (2019)]. San Bernardino County has the fourth largest population among counties in California.
2021 "The End" is Near
Slightly modified from San Bernardino County Timeline
Mining History of San Bernardino County
San Bernardino County is not only the largest county in California, but it is the largest in the United States. As a county it has been uniquely endowed with rich mineral deposits. Large deposits of gold have been mined at ...
San Bernardino County
Incorporated Areas
- San Bernardino (County Seat)
- Adelanto
- Apple Valley
- Barstow
- Big Bear Lake
- Blythe
- Hesperia
- Needles
- Victorville
- Yucca Valley
Other Communities
- Amboy
- Angelus Oaks
- Argus
- Arrowbear Lake
- Bagdad
- Baker
- Baldy Mesa
- Big Bear
- Big Bear City
- Blue Jay
- Cadiz
- Cajon Junction
- Cima
- Crestline
- Daggett
- Earp
- Essex
- Fawnskin
- Fort Irwin
- Goffs
- Green Valley Lake
- Halloran Springs
- Helendale
- Hinkley
- Hodge
- Johannesburg
- Joshua Tree
- Kelso
- Lake Arrowhead
- Lake Gregory
- Landers
- Lockhart
- Lucerne Valley
- Ludlow
- Morongo Valley
- Mountain Pass
- Newberry Springs
- Nipton
- Oak Hills
- Oro Grande
- Parker Dam
- Phelan
- Pioneertown
- Red Mountain
- Saltus
- Silver Lakes
- Trona
- Vidal
- Vidal Junction
- Wrightwood
- Yermo