--
Mojave River
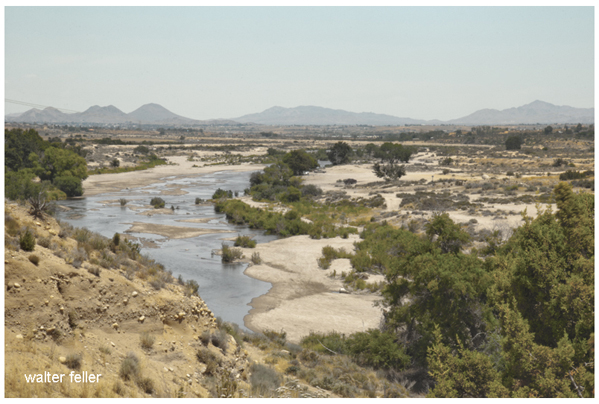

Mojave River along Hesperia
The Mojave River is unique as for most of its length water flows below ground, under the sand and instead of flowing toward the ocean as rivers do, the Mojave flows inland, terminating in the middle of the desert.
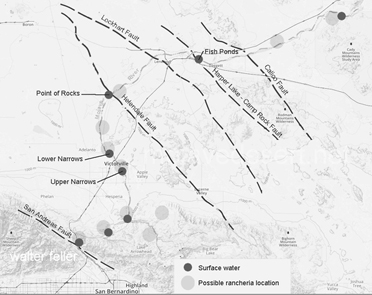
The ephemeral waters of the Mojave originate in the watershed of the San Bernardino Mountains. Water gathers from north of the ridgeline and flow down a series of creeks and washes, either underground, or combine in either Deep Creek or Miller Creek, the main above ground sources of the Mojave River before it slips beneath the surface.
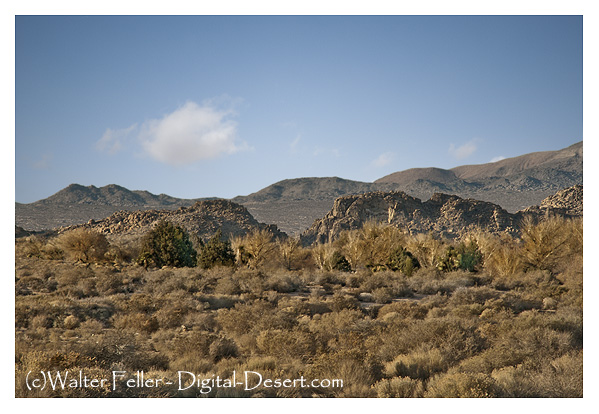

Upper Mojave River Narrows
The Mojave waters do come above ground. Usually, the river flow can be seen at the upper narrows between Victorville and Apple Valley, then downstream past Barstow at the lower narrows as the river begins its way through Afton Canyon. The river winds down the canyon and seeps into the sand disappearing before it reaches Soda Lake near Baker.
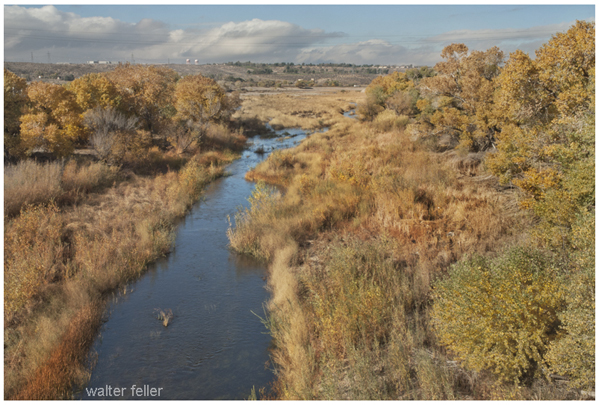
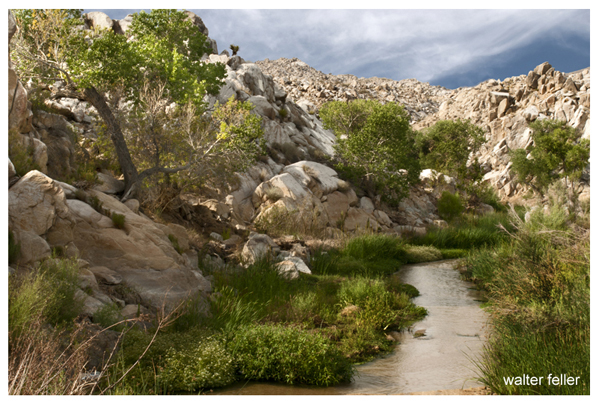
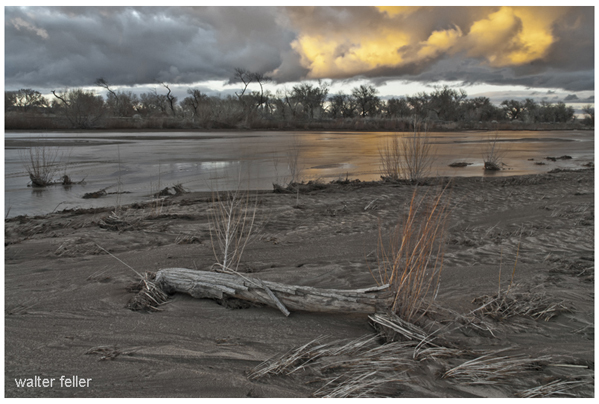
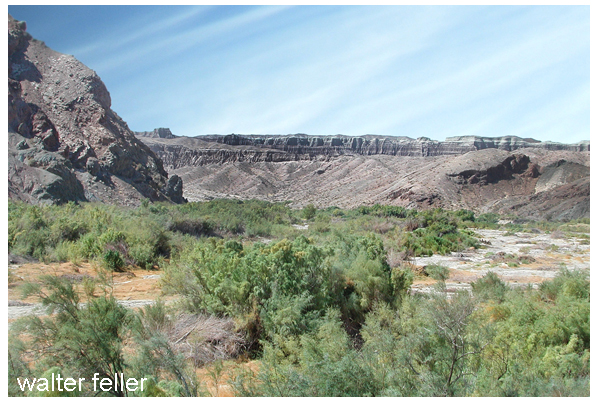




Afton Canyon
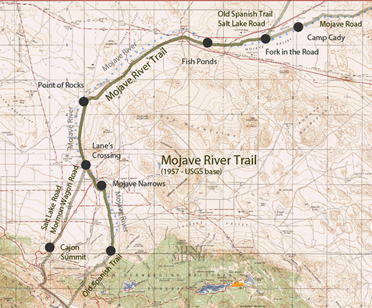
The Mojave Road followed along the river from Soda dry lake to the Cajon Pass. Desert Indians used this as a trade route where water could easily be found on the way to and from the coast. Later, the Old Spanish Trail and Salt Lake Trail (Mormon Road/Trail) joined up with the river near where Daggett is today.

Maps
Points of Interest
Nature
History
Geology
click for larger map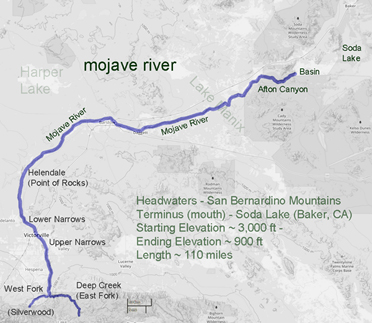
East Fork (Deep Creek)
West Fork
Ancestral Mojave River
How the Mojave River got its Name
The Broken River
Afton Canyon
Mojave River Trail & Wagon Road
Opening the Mojave River Trail