Food Pyramid
A pyramid representing trends in food consumption, with the lowest level (primary producers) having the greatest total biomass, and the higher consumer levels having successively less total biomass.The concept of a pyramid of consumers in an ecosystem helps to understand how an organism fits into a community as a whole.
Trophic structure is the pattern of movement of energy and matter through an ecosystem. It is the result of compressing a community food web into a series of trophic levels. Shown here as a food pyramid, we can see how energy moves upward through the system.
Typical Desert Food Pyramid
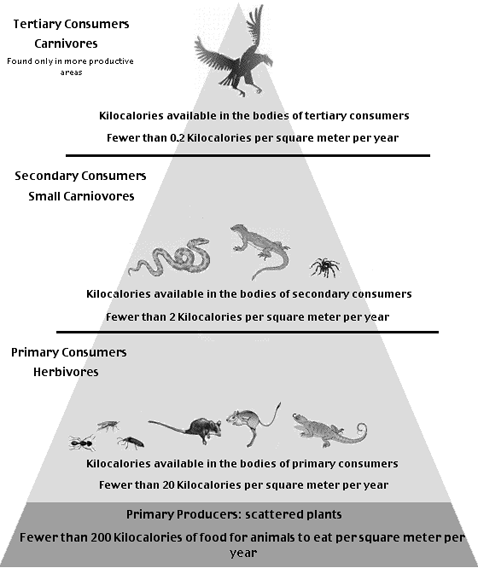
4th Trophic Level:Tertiary Consumers
Carnivores - These are high level consumers, carnivores that will eat other carnivores.Secondary Consumers
Small Carnivores - The predators are the secondary consumers. They occupy the third trophic level. Again we see cold-blooded animals, such as snakes, insect-eating lizards, and tarantualas. Only about 2 Kilocalories per square meter per year are stored in their bodies. In the harsher desert environments, they are the top predators.Primary Consumers
Herbivores These animals are usually small and eat little. Many are insects, or reptiles, who are cold blooded and who use less energy to maintain their bodies than mammals and birds do. As food for predators, they provide about 20 Kilocalories per square meter per year for predators. Including: Ants and other insects, rats and mice, some reptiles the largest of which are the tortoise and chuckwalla.Primary Producers
Plants - These are plants that make food through photosynthesis. Limited by the availability of water, they produce fewer than 200 Kilocalories of food for the animals for each square meter each year. Including: Trees, shrubs, cactus, wildflowers, grassesDesert Food Webs
The interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem. These relationships can be complex; some organisms may ...