Mono - Section 341D
This section is in the western part of the Great Basin, just east of the Sierra Nevada. It is in MLRA 26.Geomorphology. Isolated ranges (largely dissected block mountains) separated by aggraded desert plains (alluvial fans and basins). Basin and Range geomorphic province.
Lithology. Cenozoic volcanic rocks and alluvial deposits, Paleozoic sedimentary and volcanic rocks, and Mesozoic granitic rocks.
Soil Taxa. Alfisols, Aridisols, Entisols, Inceptisols, Mollisols and Vertisols in combination with mesic, frigid or cryic soil temperature regimes and aridic, xeric, or aquic soil moisture regimes.
Vegetation. Predominant potential natural communities includes the Big sagebrush series, Utah juniper series, Singleleaf pinyon series, Shadscale series, Low sagebrush series, Jeffrey pine series, White fir series, Aspen series and Bristlecone pine series (subalpine series).
The following series are found throughout the section and are not restricted to or extensive in any subsection. Series dominated by exotic plants are not listed under subsections unless they are extensive and stable.
Series dominated by exotic plants: Cheatgrass series, Crested wheatgrass series, Introduced perennial grassland series, Kentucky bluegrass series and Tamarisk series.Fauna. Pronghorn and mountain sheep were commonly found in the section. Presently pronghorn are limited to a few reintroduced herds and mountain sheep are found on a few high mountains.
Series that can occur in all subsections, but are not extensive: Bulrush series, Bulrush - cattail series, Bur-reed series, Cattail series, Cordgrass series, Ditch-grass series, Duckweed series, Mosquito fern series, One-sided bluegrass series, Pondweeds with floating leaves series, Pondweeds with submerged leaves series, Sedge series and Spikerush series.
Series restricted to riparian settings: Arroyo willow series, Black cottonwood series, Black willow series, Common reed series, Fremont cottonwood series, Mixed willow series, Narrowleaf willow series, Red willow series and Water birch series.
Mammals include mule deer, mountain lion, bobcat, coyote, jackrabbits and chipmunks.
Birds include eagles, hawks, northern goshawk, nighthawks (see raptors), common poorwill, sage grouse, sparrows and gnatcatchers. Mono Lake provides habitat to a wide variety of shorebirds and migrating waterfowl. It is also the second largest California gull rookery in the world.
Reptiles include sagebrush lizard, desert horned lizard, western fence lizard and spadefoot toad are common in the section.
Elevation. 4400 to 14200 feet.
Precipitation. 5 to 30 inches.
Temperature. 30° to 58°F.
Growing Season. 20 to 200 days.
Surface Water Characteristics. Few rapid flowing rivers and streams. Rivers and streams flow in deeply incised canyons with bedrock controlled channels (higher elevations) to alluvial channels (lower elevations) that terminate in basins or lakes within the area, or in basins and lakes in the Mojave Desert, Bonneville Basin and Northwestern Basin and Range sections. Several large lakes occur within the section.
Disturbance Regimes.
Fire: Fires are infrequent, low, moderate and high intensity surface or stand replacing fires.Land Use. Composition and successional sequence of some communities has changed because of plant and animal species introduced between the mid 1800’s and early 1900’s related to mining, grazing, forestry and recreational activities.
Volcanic Activity: Contains locations with eruptive activity (lava flows and ash fall) within the past 200 years.
Seismic Activity: Seismically active area with strong shaking and ground rupture.
Cultural Ecology. Humans have been utilizing the section
for 10,000 years, and have been an integral part of its ecology for 3,000
to 5,000 years. Extensive prehistoric procurement and processing
of obsidian resources have left vast areas pockmarked and littered with
lithic debitage; extensive procurement and processing of piagi and pine
nuts have modified vast areas of Jeffrey pine and pinyon. Historic
mining booms beginning in the late 1800’s and water diversion projects
for the Los Angeles basin beginning in the early 1900’s resulted in additional
ecological modifications. Contemporary attitudes and beliefs emphasize
amenity values. Human environment is characterized by a rural lifestyle
of open space and out-door leisure activity. Recreation is the primary
economic emphasis, trailed by government employment, lumbering, mining,
and grazing.
Native Cultural Notes:
Owens Valley Paiute
Western Mono Indians
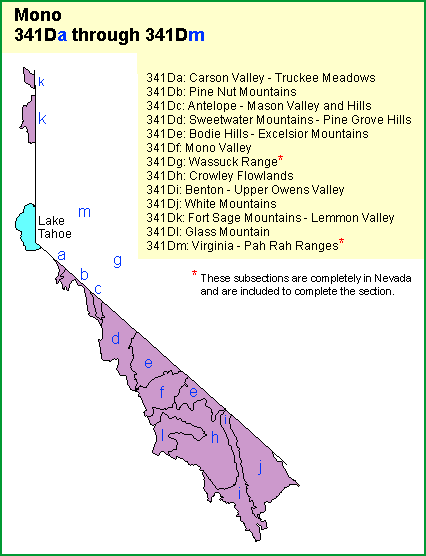
The Mono section is divided into 13 subsections
A- Carson Valley - Truckee Meadows
... consists mostly of an alluvial plain in Truckee Meadows and the Spanish Springs, Washoe, Carson, and ...
B- Pine Nut Mountains
... comprises the Pine Nut Mountains. It has a temperate to cold, semi-arid climate.
C- Antelope - Mason Valley and Hills
... includes Mason and Smith Valleys between the Pine Nut Mountains on the west and the Wassuck Range on the east, ...
D- Sweetwater Mountains - Pine Grove Hills
... includes the Sweetwater Mountains, which are between the West Walker and East Walker Rivers; the Wellington and ...
E- Bodie Hills Excelsior Mountains
... includes the Excelsior Mountains; the Bodie, Anchorite, and Adobe Hills; and the Alkali and Huntoon Valleys.
F- Mono Valley
... consists of the lake plain around Mono Lake, which is at the base of the steep eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada.
G- Wasuck Mountains*
... comprises the Wassuck Range, which is just west of Walker Lake.
H- Crowley Flowlands
... includes the Benton Range, Blind Spring Hill, Granite Mountain, Mono Craters, Volcanic Tableland south of the Benton Range,..
I- Benton - Upper Owens Valley
... includes the Queen, Benton, Hammil, Chalfant, and upper part of the ...
J- White Mountains
... comprises the White Mountains, the highest mountain range in the Great Basin. It has ...
K- Fort Sage Mountains - Lemmon Valley
... includes mountains, hills, and valleys between the Sierra Nevada on the west and the Pah Rah Range and Pyramid Lake on the east.
L- Glass Mountain
encompasses volcanic peaks and craters on a volcanic plain northeast of the Sierra Nevada below Mammoth Pass, ...
M- Virginia - Pah Rah Ranges*
... comprises the Virginia Range south of the Truckee River and the Pah Rah Range north of the Truckee River.
*Subsections completely in Nevada