|
|
Antelope Valley:
Antelope Valley Geography
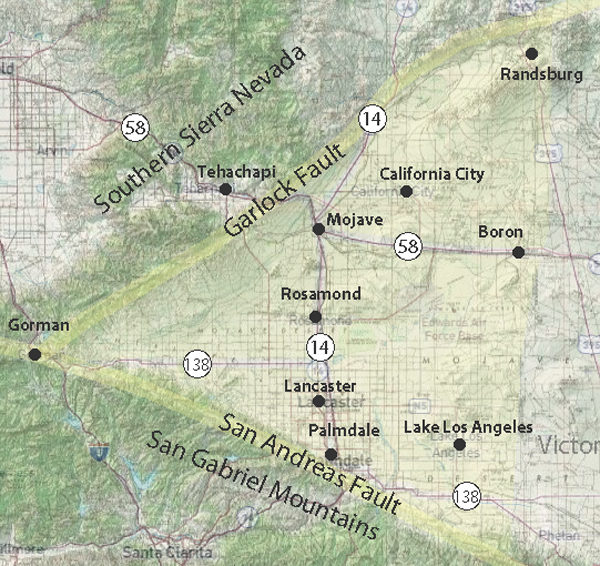
Wedged between the San Andreas and Garlock faults, the Antelope Valley comprises the westernmost end of the Mojave Desert.
The valley, north of the San Gabriel Mountains (San Andreas Fault)
and south of the Garlock fault and the southern Sierra Nevada (Tehachapi) Mountains, this desert ecosystem spans approximately 2,200 square miles (5,698 km2).
The topography is mostly alluvial plain and pediment scattered with low mountains and hills. (ed)
|
San Gabriel Mountains
To the millions of Los Angeles area residents who live within an hour"s drive and to visitors from all over the world, the Angeles National Forest provides a thousand square miles of ...
Garlock Fault
The Garlock Fault is the defining fault between the Mojave Desert and ...
San Andreas Fault
The presence of the San Andreas fault was brought dramatically to world attention on April 18, 1906, when sudden displacement along the fault produced ...
High Desert Plains and Hills
This subsection consists of the western Mojave Desert, which is mostly alluvial plain and pediment, with relatively small areas of hills and low mountains. It includes ...
|
