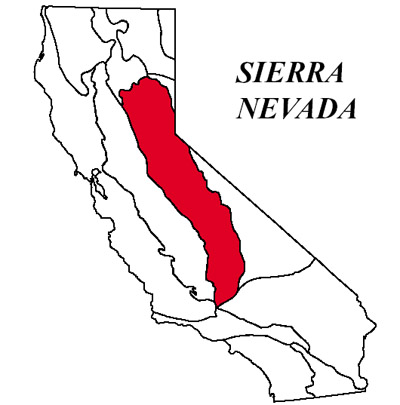
Sierra Nevada Geomorphic Province
The Sierra is a tilted fault block nearly 400 miles long. Its east face is a high, rugged multiple scarp, contrasting with the gentle western slope (about 2 ) that disappears under sediments of the Great Valley. Deep river canyons are cut into the western slope. Their upper courses, especially in massive granites of the higher Sierra, are modified by glacial sculpturing, forming such scenic features as Yosemite Valley. The high crest culminates in Mt. Whitney with an elevation of 14,495 feet above sea level near the eastern scarp. The metamorphic bedrock contains goldbearing veins in the northwest trending Mother Lode. The northern Sierra boundary is marked where bedrock disappears under the Cenozoic volcanic cover of the Cascade Range.
Ecology
Sierra Nevada
This section is the temperate to very cold parts of the Sierra Nevada, which is a north-northwest aligned mountain range that is much steeper on the east than on the west side.Sierra Nevada Foothills
This section comprises the hot foothills of the Sierra Nevada, and the southwestern end of the Cascade Ranges, adjacent to the Great Valley.