==
Hoover Dam
Frequently Asked Questions - Power
Hoover Dam provides generation of low-cost hydroelectric power for use in Nevada, Arizona, and California. Hoover Dam alone generates more than 4 billion kilowatt-hours a year - enough to serve 1.3 million people. From 1939 to 1949, Hoover Powerplant was the world's largest hydroelectric installation; today, it is still one of the country's largest.
Hydroelectricity is a clean, renewable source of energy that does not result in air pollution, chemical runoff, or toxic waste disposal.
Where is the powerplant located?
In a U-shaped structure at the base of the dam. Each powerplant wing is 650 feet long. In all of the galleries of the plant there are 10 acres of floor space.
What is the capacity of the Hoover Powerplant?
There are 17 main turbines in Hoover Powerplant. The original turbines were all replaced through an uprating program between 1986 and 1993. With a rated capacity of 2,991,000 horsepower, and two station-service units rated at 3,500 horsepower each, for a plant total of 2,998,000 horsepower. The plant has a nameplate capacity of about 2,080 megawatts. This includes the two station-service units, which are rated at 2.4 megawatts each.
How does the water reach the turbines?
Through four penstocks, two on each side of the river. Wicket gates control water delivery to the units.
Under what heads do the turbines operate?
Maximum head (vertical distance the water travels), 590 feet; minimum, 420 feet; average, 510 to 530 feet.
When were the power installations in the plant completed, and of what do they consist?
Installation was completed in 1961. With the uprating completed in 1993, there are fifteen 178,000 horsepower, one 100,000 horsepower, and one 86,000 horsepower Francis-type vertical hydraulic turbines. There are thirteen 130,000 kilowatt, two 127,000 kilowatt, one 61,500 kilowatt, and one 68,500 kilowatt generators. All machines are operated at 60 cycles. There are also two 2,400 kilowatt station-service units driven by Pelton water wheels. These provide electrical energy for lights and for operating cranes, pumps, motors, compressors, and other electrical equipment within the dam and powerplant.
How was the powerplant machinery transported from the canyon rim to
the powerplant?
An electrically operated cableway of 150 tons rated capacity, with a 1,200-foot span across the canyon, lowered all heavy and bulky equipment. The cableway is still used when necessary.
How much energy does Hoover Powerplant produce on a yearly basis?
The average annual net generation for Hoover Powerplant for 1947 through 2005 was about 4.4 billion kilowatt-hours. The ten-year annual average for 1996 through 2005 was about 4.8 billion kilowatt-hours. The maximum annual net generation at Hoover Powerplant was 10,348,020,500 kilowatt-hours in 1984, while the minimum annual net generation since 1940 was 2,648,224,700 kilowatt-hours in 1956.
What is a kilowatt-hour?
It is a unit of work or energy equal to that done by one kilowatt of power acting for one hour. A kilowatt is 1,000 watts or 1.34 horsepower.
Who operates and maintains the powerplant?
The powerplant is operated and maintained by the Bureau of Reclamation.
Who are the principal contractors for energy?
The States of Arizona and Nevada; City of Los Angeles; Southern California Edison Co.; Metropolitan Water District of Southern California; California cities of Glendale, Burbank, Pasadena, Riverside, Azusa, Anaheim, Banning, Colton, and Vernon; and the city of Boulder City, Nevada.
How is the firm energy generated at Hoover Dam allocated?
Arizona - 18.9527 percent
Nevada - 23.3706 percent
Metropolitan Water District of Southern California - 28.5393 percent
Burbank, CA - 0.5876 percent
Glendale, CA - 1.5874 percent
Pasadena, CA - 1.3629 percent
Los Angeles, CA - 15.4229 percent
Southern California Edison Co. - 5.5377 percent
Azusa, CA - 0.1104 percent
Anaheim, CA - 1.1487 percent
Banning, CA - 0.0442 percent
Colton, CA - 0.0884 percent
Riverside, CA - 0.8615 percent
Vernon, CA - 0.6185 percent
Boulder City, NV - 1.7672 percent
How is the income from the sale of energy used?
To pay all operation and maintenance expenses and to repay the major part of the construction cost of the dam and powerplant, at interest not exceeding 3 percent. The cost of construction completed and in service by 1937 was repaid on May 31, 1987. All other costs, except those for flood control, will be repaid within 50 years of the date of installation or as established by Congress. Repayment of the $25 million construction cost allocated to flood control is currently deferred. In addition, Arizona and Nevada each receive $300,000 annually in lieu of taxes.
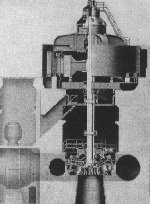
What are the primary parts of a generating unit?
The Exciter
The RotorThe Stator
The Shaft
The Turbine
The exciter is itself a small generator that makes electricity, which is sent to the rotor, charging it with a magnetic field.
The rotor is a series of electromagnets, also called poles. The rotor is connected to the shaft, so that the rotor rotates when the shaft rotates.
The stator is a coil of copper wire. It is stationary.
The shaft connects the exciter and the rotor to the turbine.
Water strikes the turbine causing it to spin. Hoover Dam uses Francis turbines.
How is electricity made?
Electricity is produced as the magnets of the rotors spin past the stationary wiring of the stator. This concept was discovered by scientist Michael Faraday in 1831 when he found that electricity could be created by rotating magnets within copper coils.
Source - U.S. Department of the Interior - Bureau of Reclamation